Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Science
Related: About this forumHere's How Colossal Galaxy Clusters Reveal Dark Matter Secrets
By Paul Sutter 9 hours ago Science & Astronomy
Galaxy clusters rule the dark universe.
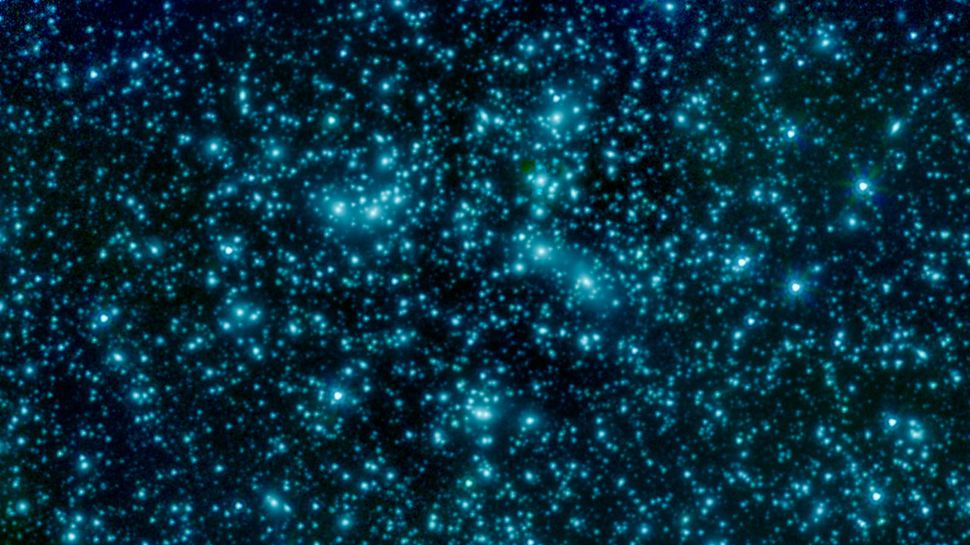

The star cluster Abell 2744, also known as Pandora's Cluster, as imaged by the Spitzer Space Telescope in infrared.(Image: © NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Clusters of galaxies hold the prestigious title of "largest gravitationally bound structures in the universe," which is no small feat. Tipping the scales at a million billion times the mass of the sun, these bustling cities of the cosmos aren't going anywhere anytime soon. That's the whole point of being gravitationally bound: The clusters' gravity allows them to resist the expansion of the universe and keep their stuff generally together for a very long time.
As their name suggests, galaxy clusters host a lot of galaxies, typically anywhere from 100 to over 1,000. And yet, when you add up the masses of all the member galaxies, you get less than 1% of the total cluster mass. The galaxies aren't alone, thankfully; they're joined by a hot, thin plasma that threads and winds its way throughout the cluster. But even that plasma accounts for only 10% of the cluster mass.
Most of the mass of a cluster of galaxies, and the thing that really keeps them gravitationally bound, doesn't come from the galaxies or gas that we can detect. In fact, we can't see it at all. The mystery mass is dark matter — and galaxy clusters give us some of the strongest clues as to the nature of this mysterious component of the cosmos.
Fritz's surprise
Back in the 1930s, when nobody knew much about anything cosmological, astronomer Fritz Zwicky was studying the Coma cluster, a gang of about 1,000 galaxies sitting around 320 million light-years away from Earth. Fritz was especially interested in the motions of those galaxies, and he found something rather peculiar. The galaxies were moving all right … fast. Way fast. Too fast.
More:
https://www.space.com/galaxy-clusters-rule-dark-universe.html
InfoView thread info, including edit history
TrashPut this thread in your Trash Can (My DU » Trash Can)
BookmarkAdd this thread to your Bookmarks (My DU » Bookmarks)
2 replies, 675 views
ShareGet links to this post and/or share on social media
AlertAlert this post for a rule violation
PowersThere are no powers you can use on this post
EditCannot edit other people's posts
ReplyReply to this post
EditCannot edit other people's posts
Rec (1)
ReplyReply to this post
2 replies
 = new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
= new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
Here's How Colossal Galaxy Clusters Reveal Dark Matter Secrets (Original Post)
Judi Lynn
Jun 2019
OP
RainCaster
(10,857 posts)1. What a frustrating waste of time!
I wanted to know so much more that this article told me. Thanks Judi, now I'll be spending the remainder of my evening tracking down the conclusions of this thread.
RainCaster
(10,857 posts)2. Thanks, though, it is very cool