kristopher
kristopher's JournalEDF ‘in big trouble’ says French nuclear expert
Financial problems facing EDF could force the French energy giant to pull out of the £14bn project to build the first of a new generation of nuclear power plants in Britain, a French expert has warned.
10:00PM BST 08 Apr
Mycle Schneider, a former energy adviser to the French government, questioned whether EDF could finance the investment.
“EDF is in big trouble. The whole of the nuclear power industry in France is in big trouble,” he told BBC Radio 4's Today programme.
...President Hollande is seen as a pivotal figure because he wants state controlled EDF to curb its nuclear power ambitions and invest heavily in improving safety at plants in France as well as giving a higher priority to renewable energy.
Negotiations on a deal between EDF and the (UK) Government over the construction of a massive plant at Hinkley Point in Somerset are deadlocked because the two sides have failed to agree on a price for electricity and a range of other guarantees...
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/newsbysector/energy/9978548/EDF-in-big-trouble-says-French-nuclear-expert.html
Yet Another Country's Chief Nuclear Regulator Questions Nuclear Plant Safety
Monday, 08 April 2013 | Kumar Chellappan | Chennai
Against the backdrop of the arrest of Sergei Shutov, a director of Zio-Podolsk, a subsidiary of Rosatom, on charges of corruption, fraud and supplying cheap Ukrainian steel blanks and steam generators in nuclear reactors, former chairman of Atomic Energy Regulatory Board Dr A Gopalakrishnan has demanded an immediate investigation into the safety of the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant in India as it was Podolsk that had supplied components for the reactor.
He demanded constitution of an independent body of nuclear engineering specialists to ascertain the KNPP’s safety.
This is the first time in the history of the Indian nuclear establishment, a former chief regulator, who is respected all over the nuclear world for his no-nonsense approach, has questioned the claims of the Government that the plant is foolproof and “greener than even green”.
Gopalakrishnan, a nuclear power engineer with more than five decades of experience, said nothing was right with the 1,000 MW reactor built with Russian assistance. “The inordinate delay in the commissioning of the plant and the silence of the country’s nuclear regulator, Atomic Energy Regulatory Board, has substantiated our doubts about the safety and security of the plant,” said the country’s former chief nuclear regulator.
...
http://www.dailypioneer.com/todays-newspaper/kudankulam-n-plant--in-danger-supplier--held-for-shoddy-parts.html
Here is former NRC Commission Chair Jazcko expressing reservations yesterday about the US nuclear fleet.
By MATTHEW L. WALD
Published: April 8, 2013
WASHINGTON — All 104 nuclear power reactors now in operation in the United States have a safety problem that cannot be fixed and they should be replaced with newer technology, the former chairman of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission said on Monday. Shutting them all down at once is not practical, he said, but he supports phasing them out rather than trying to extend their lives.
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/04/09/us/ex-regulator-says-nuclear-reactors-in-united-states-are-flawed.html?_r=0
Also see this interview with Jazcko by Asahi Shimbun 2 weeks ago: http://www.democraticunderground.com/112738667
Japan's quake-crippled nuclear plant "losing faith" in leaking water pits
Reuters
TOKYO (Reuters) - The company that runs a Japanese nuclear power plant destroyed by a tsunami two years ago said on Tuesday it was losing faith in temporary storage pits for radioactive water - but it doesn't have anywhere else to put it.
Tokyo Electric Power Co (Tepco) said it had found a new leak at one of the pits at the Fukushima Daiichi plant. Three out of seven storage pits are now leaking, compounding clean-up difficulties after the world's worst nuclear crisis in 25 years.
"We cannot deny the fact that our faith in the underwater tanks is being lost," Tepco general manager Masayuki Ono told a hastily arranged news conference.
"We can't move all the contaminated water to above ground (tanks) if we opt not to use the underground reservoirs," Ono said. "There isn't enough capacity and we need to use what is available."
...
http://news.yahoo.com/leak-found-fukushima-plant-water-storage-pool-regulator-044042392--finance.html
Nope.
You can't turn off coal without also turning off nuclear - the economic fundamentals of both are the same. Centralized largescale "baseload" generation is a product of those economic fundamentals. It isn't an unalterable law of nature that all energy delivery systems must duplicate. In fact, a distributed grid provides greater resilience, durability, and reliability. When it is made up of renewables, it eliminates fuel insecurity.
There are far more lessons from Fukushima than what you've noted, and the problem Jazcko is talking about with regulatory capture is at the top of the list. Nuclear ISN'T safe because human are not perfect and we do not design perfect systems.
If you think I'm advocating we shut all nuclear plants down now because they frighten me, you're mistaken. I want a massive buildout of renewables in as short a time frame as possible. I recognize that both coal and nuclear are going to be put out of business fairly early on as renewable penetration increases; and I'm fine with that. I don't mind losing low carbon capacity of nuclear if, as Germany is doing, it is a part of the process of changing to a distributed energy system because that is the only way we are going to get rid of carbon.
Additional reading:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378775312014759
Cost-minimized combinations of wind power, solar power and electrochemical storage, powering the grid up to 99.9% of the time
http://cen.acs.org/articles/91/i13/Nuclear-Retirement-Anxiety.html
Nuclear Retirement Anxiety | April 1, 2013 Issue - Vol. 91 Issue 13 | Chemical & Engineering News
http://blog.rmi.org/blog_2013_03_26_2013_Asias_Accelerating_Energy_Revolution
Asia’s Accelerating Energy Revolution
Yes, a negative learning curve.
That's what Jazcko is describing. You find a problem, fix it and it creates potential for string of unanticipated follow on problems that you didn't think of. The upshot being the technology becomes increasingly expensive instead of steadily less expensive.
I really don't give a fig how nuclear compares to coal, and neither should you. We can acknowledge the CO2 benefit exists, so it is automatically eligible to be considered as an alternative. That is as far as we need pursue the issue of coal.
What we now seek to know is how does nuclear stack up against the other low carbon alternatives. We need to examine issues of resource availability, life cycle costs - both direct and external, safety, and the way these technologies work together in delivering the final product to the user. That last item is far more critical than most realize.
When you evaluate them, here is what you get:
You can download the full study here:
http://www.stanford.edu/group/efmh/jacobson/Articles/I/ReviewSolGW09.pdf
Here is the abstract:
Review of solutions to global warming, air pollution, and energy security
Mark Z. Jacobson
Abstract
This paper reviews and ranks major proposed energy-related solutions to global warming, air pollution mortality, and energy security while considering other impacts of the proposed solutions, such as on water supply, land use, wildlife, resource availability, thermal pollution, water chemical pollution, nuclear proliferation, and undernutrition.
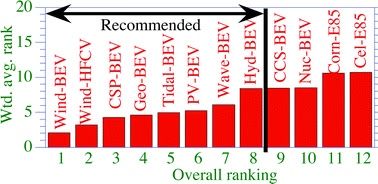
Nine electric power sources and two liquid fuel options are considered. The electricity sources include solar-photovoltaics (PV), concentrated solar power (CSP), wind, geothermal, hydroelectric, wave, tidal, nuclear, and coal with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. The liquid fuel options include corn-ethanol (E85) and cellulosic-E85. To place the electric and liquid fuel sources on an equal footing, we examine their comparative abilities to address the problems mentioned by powering new-technology vehicles, including battery-electric vehicles (BEVs), hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs), and flex-fuel vehicles run on E85.
Twelve combinations of energy source-vehicle type are considered. Upon ranking and weighting each combination with respect to each of 11 impact categories, four clear divisions of ranking, or tiers, emerge.
Tier 1 (highest-ranked) includes wind-BEVs and wind-HFCVs.
Tier 2 includes CSP-BEVs, geothermal-BEVs, PV-BEVs, tidal-BEVs, and wave-BEVs.
Tier 3 includes hydro-BEVs, nuclear-BEVs, and CCS-BEVs.
Tier 4 includes corn- and cellulosic-E85.
Wind-BEVs ranked first in seven out of 11 categories, including the two most important, mortality and climate damage reduction. Although HFCVs are much less efficient than BEVs, wind-HFCVs are still very clean and were ranked second among all combinations.
Tier 2 options provide significant benefits and are recommended.
Tier 3 options are less desirable. However, hydroelectricity, which was ranked ahead of coal-CCS and nuclear with respect to climate and health, is an excellent load balancer, thus recommended.
The Tier 4 combinations (cellulosic- and corn-E85) were ranked lowest overall and with respect to climate, air pollution, land use, wildlife damage, and chemical waste. Cellulosic-E85 ranked lower than corn-E85 overall, primarily due to its potentially larger land footprint based on new data and its higher upstream air pollution emissions than corn-E85.
Whereas cellulosic-E85 may cause the greatest average human mortality, nuclear-BEVs cause the greatest upper-limit mortality risk due to the expansion of plutonium separation and uranium enrichment in nuclear energy facilities worldwide. Wind-BEVs and CSP-BEVs cause the least mortality.
The footprint area of wind-BEVs is 2–6 orders of magnitude less than that of any other option. Because of their low footprint and pollution, wind-BEVs cause the least wildlife loss.
The largest consumer of water is corn-E85. The smallest are wind-, tidal-, and wave-BEVs.
The US could theoretically replace all 2007 onroad vehicles with BEVs powered by 73000–144000 5 MW wind turbines, less than the 300000 airplanes the US produced during World War II, reducing US CO2 by 32.5–32.7% and nearly eliminating 15000/yr vehicle-related air pollution deaths in 2020.
In sum, use of wind, CSP, geothermal, tidal, PV, wave, and hydro to provide electricity for BEVs and HFCVs and, by extension, electricity for the residential, industrial, and commercial sectors, will result in the most benefit among the options considered. The combination of these technologies should be advanced as a solution to global warming, air pollution, and energy security. Coal-CCS and nuclear offer less benefit thus represent an opportunity cost loss, and the biofuel options provide no certain benefit and the greatest negative impacts.
What is most important to me, however, is the fact that renewables integrate differently than centralized generation. Economics are the tool that facilitates change - and nuclear doesn't alter the economic landscape that is built around coal. In fact, nuclear re-enforces the market position of coal by crowding out the types of generation that nibble away the market share of all centralized large scale thermal plants - renewables.
This thread shows how the market works to allow zero-energy cost renewables take market share away from all sources of generation with fuel costs.
http://www.democraticunderground.com/?com=view_post&forum=1127&pid=11729
The plans of the utilities in the US that are intent on building nuclear plants show that they have absolutely no intention of reducing their consumption of coal. See this summary of their plans:
Clinging to Dirty Energy in the South – a by-the-numbers look from the Institute of Southern Studies http://www.southernstudies.org/2011/10/institute-index-clinging-to-dirty-energy-in-the-south.html
The New Nuclear Power is Ruining Climate Protection Efforts and Harming Customers Report shows Southeast utilities plan not to replace coal-fired power, but to add nuclear capacity despite falling demand – while jacking up rates and blocking clean energy advances http://www.ncwarn.org/wp- content/uploads/2011/10/NCW-NuclearClimate_web.pdf
Can you explain the justification for nuclear if it does not have a market mechanism to shut down coal plants? I can't. Especially considering it has the risk of catastrophic failure lingering over every plant every day. We aren't going to be as lucky every time as we were with Fukushima; have you considered what would have happened if the winds had been steady out of the NNE instead of the W and SSE?
edited to fix links and formatting tags
Move is on to make concrete plans for 100% renewables
By Paul Gipe, Contributor
April 4, 2013
Increasingly countries and regions are leapfrogging timid renewable targets and moving toward full 100 percent integration of renewables into electricity supply. Some thought leaders, politicians, and advocates are moving even further, suggesting 150 percent, even 300 percent renewable electricity generation to meet not only electricity supply but also heat and transport.
<snip>
Meanwhile, Danes continued to erect ever more wind turbines throughout the 1990s. Soon Denmark was closing on 20 percent of supply from wind energy alone and it became apparent — again — that our targets were too modest.
<snip>
The list of what was once unimaginable continues to grow. Portugal’s 10 million people produced more than half their electricity in 2010 from their own indigenous renewable resources. Spain’s 40 million people meet one-third of their electrical consumption from renewables.
<snip>
On the panel were two long-time renewable pioneers, Preben Maegaard from Denmark, and Johannes Lackmann from Germany. Independent of each other, both had come to the same conclusion. To address climate change and energy security, we must move well beyond 100 percent renewable energy in electricity supply and build an integrated network capable of using more than 150% renewable energy, up to as much as 300 percent renewable energy to offset fossil fuels in transportation, and heating.
Read entire piece at:
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/04/100-percent-renewable-vision-building?cmpid=WNL-Friday-April5-2013
Xposted from Good Reads
In case you missed it - Massive US Govt study shows todays renewables can power US
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory's (NREL) Renewable Electricity Futures Study (RE Futures) is an initial investigation of the extent to which renewable energy supply can meet the electricity demands of the continental United States over the next several decades. This study explores the implications and challenges of very high renewable electricity generation levels—from 30% up to 90%, focusing on 80%, of all U.S. electricity generation—in 2050. At such high levels of renewable electricity generation, the unique characteristics of some renewable resources, specifically geographical distribution and variability and uncertainty in output, pose challenges to the operability of the nation's electric system.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory's (NREL) Renewable Electricity Futures Study (RE Futures) is an initial investigation of the extent to which renewable energy supply can meet the electricity demands of the continental United States over the next several decades. This study explores the implications and challenges of very high renewable electricity generation levels—from 30% up to 90%, focusing on 80%, of all U.S. electricity generation—in 2050. At such high levels of renewable electricity generation, the unique characteristics of some renewable resources, specifically geographical distribution and variability and uncertainty in output, pose challenges to the operability of the nation's electric system.
Key Findings
- Renewable electricity generation from technologies that are commercially available today, in combination with a more flexible electric system, is more than adequate to supply 80% of total U.S. electricity generation in 2050 while meeting electricity demand on an hourly basis in every region of the country.
- Increased electric system flexibility, needed to enable electricity supply and demand balance with high levels of renewable generation, can come from a portfolio of supply- and demand-side options, including flexible conventional generation, grid storage, new transmission, more responsive loads, and changes in power system operations.
- The abundance and diversity of U.S. renewable energy resources can support multiple combinations of renewable technologies that result in deep reductions in electric sector greenhouse gas emissions and water use.
- The direct incremental cost associated with high renewable generation is comparable to published cost estimates of other clean energy scenarios. Improvement in the cost and performance of renewable technologies is the most impactful lever for reducing this incremental cost.
RE Futures provides initial answers to important questions about the integration of high penetrations of renewable electricity technologies from a national perspective, focusing on key technical implications. The study explores electricity grid integration using models with unprecedented geographic and time resolution for the contiguous United States to assess whether the U.S. power system can supply electricity to meet customer demand on an hourly basis with high levels of renewable electricity, including variable wind and solar generation.
RE Futures, funded by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, is a collaboration with more than 110 contributors from 35 organizations including national laboratories, industry, universities, and non-governmental organizations.
As the most comprehensive analysis of high-penetration renewable electricity of the continental United States to date, the study can inform broader discussion of the evolution of the electric system and electricity markets toward clean systems. RE Futures results indicate that renewable generation could play a more significant role in the U.S. electricity system than previously thought and that further work is warranted to investigate this clean generation pathway.
Links to download full study here: http://www.nrel.gov/analysis/re_futures/
100 Percent Renewable Vision Building
100 Percent Renewable Vision BuildingBy Paul Gipe, Contributor
April 4, 2013
Increasingly countries and regions are leapfrogging timid renewable targets and moving toward full 100 percent integration of renewables into electricity supply. Some thought leaders, politicians, and advocates are moving even further, suggesting 150 percent, even 300 percent renewable electricity generation to meet not only electricity supply but also heat and transport.
<snip>
Meanwhile, Danes continued to erect ever more wind turbines throughout the 1990s. Soon Denmark was closing on 20 percent of supply from wind energy alone and it became apparent — again — that our targets were too modest.
<snip>
The list of what was once unimaginable continues to grow. Portugal’s 10 million people produced more than half their electricity in 2010 from their own indigenous renewable resources. Spain’s 40 million people meet one-third of their electrical consumption from renewables.
<snip>
On the panel were two long-time renewable pioneers, Preben Maegaard from Denmark, and Johannes Lackmann from Germany. Independent of each other, both had come to the same conclusion. To address climate change and energy security, we must move well beyond 100 percent renewable energy in electricity supply and build an integrated network capable of using more than 150% renewable energy, up to as much as 300 percent renewable energy to offset fossil fuels in transportation, and heating.
Read entire piece at:
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/04/100-percent-renewable-vision-building?cmpid=WNL-Friday-April5-2013
Renewables to Exceed Fossil Fuels in European Generation by 2020
By Rachel Morison, Bloomberg
April 3, 2013
LONDON -- Europe's share of generation capacity using renewable sources will rise to at least 40 percent by 2020, exceeding capacity fueled by coal, natural gas and oil, according to the region's grid operators group Entsoe.
Renewable electricity output capacity will grow by about 50 percent to 512 gigawatts by the end of the decade, Entsoe said in a report published today. Generation capacity using fossil fuels may rise 0.7 percent to 471 gigawatts in the same period. Nuclear production accounts for most of the rest, according to Entsoe’s figures.
The European Union aims to generate 20 percent of its power from renewable energy by 2020 and cut reliance on carbon-heavy coal and oil output. Carbon emissions fell 1.4 percent in Europe last year as the 27-nation bloc worked toward reducing emissions by 20 percent from 1990 levels by 2020.
“Wind, solar and biomass power plants are expected to increase, while the share of hydropower plants is expected to decrease,” Entsoe said. The increasing volume of variable renewable generation urgently requires “complementary measures” to ensure the balancing of the system, it said.
Norway will remain the country with the most power produced from renewables with 96 percent in 2020...
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/04/renewables-to-exceed-fossil-fuels-in-european-generation-by-2020??cmpid=SolarNL-Thursday-April4-2013
Old EV Batteries as Solar Storage Solution
<snip>
...The potential of car batteries
One of the ways utilities are looking to store energy on their massive infrastructures is using old hybrid car batteries tied together to create community energy storage (CES). It’s a development being studied right now by a partnership of Nissan North America, the ABB power and technology company, the UK company 4R Energy and investment firm Sumitomo Corporation of America.
Even after the electric car’s battery has served its purpose, it typically can still operate at 70% of its capacity.
Most lithium-ion battery packs that power vehicles such as Nissan’s all-electric car, the LEAF, have an estimated life of about 10 years, just shy of the average age of an automobile these days. But even after the electric car’s battery has served its purpose, it typically can still operate at 70% of its capacity and when you tie a handful of them together, Nissan and ABB think the combined storage will supply a collection of homes with power.
ABB has already demonstrated a prototype modular CES unit using five used Chevrolet Volt batteries. That demonstration unit also used depleted batteries that had reached the end of their useful automotive life, which means only 30% of their life had been used.
“This leaves a tremendous amount of life that can be applied to other applications like powering a structure before the battery is recycled,” Pablo Valencia, GM senior manager of battery lifecycle management in stated in a press release....
ETA: Not sure how to turn off smilies. They are messing up the link at the /colon oh/ so I've broken it. If you want to read the article, put the two sections together.
http://www.solarnovus.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=6339: old-ev-batteries-as-solar-storage-solution&catid=38:application-tech-features&Itemid=246
Profile Information
Member since: Fri Dec 19, 2003, 02:20 AMNumber of posts: 29,798