Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Dennis Donovan
Dennis Donovan's Journal
Dennis Donovan's Journal
April 21, 2019
183 Years Ago Today; The Battle of San Jacinto
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_San_Jacinto

The Battle of San Jacinto – 1895 painting by Henry Arthur McArdle (1836–1908)
The Battle of San Jacinto (Spanish: Batalla de San Jacinto), fought on April 21, 1836, in present-day Harris County, Texas, was the decisive battle of the Texas Revolution. Led by General Sam Houston, the Texian Army engaged and defeated General Antonio López de Santa Anna's Mexican army in a fight that lasted just 18 minutes. A detailed, first-hand account of the battle was written by General Houston from Headquarters of the Texian Army, San Jacinto, on April 25, 1836.[3] Numerous secondary analyses and interpretations have followed, several of which are cited and discussed throughout this entry.
General Santa Anna, the President of Mexico, and General Martín Perfecto de Cos both escaped during the battle. Santa Anna was captured the next day on April 22 and Cos on April 24, 1836. After being held about three weeks as a prisoner of war, Santa Anna signed the peace treaty that dictated that the Mexican army leave the region, paving the way for the Republic of Texas to become an independent country. These treaties did not specifically recognize Texas as a sovereign nation, but stipulated that Santa Anna was to lobby for such recognition in Mexico City. Sam Houston became a national celebrity, and the Texans' rallying cries from events of the war, "Remember the Alamo!" and "Remember Goliad!" became etched into Texan history and legend.
<snip>
San Jacinto
The area along Buffalo Bayou had many thick oak groves, separated by marshes. This type of terrain was familiar to the Texians and quite alien to the Mexican soldiers. Houston's army, comprising 900 men, reached Lynch's Ferry mid-morning on April 20; Santa Anna's 700-man force arrived a few hours later. The Texians made camp in a wooded area along the bank of Buffalo Bayou; while the location provided good cover and helped hide their full strength, it also left the Texians no room for retreat. Over the protests of several of his officers, Santa Anna chose to make camp in a vulnerable location, a plain near the San Jacinto River, bordered by woods on one side, marsh and lake on another. The two camps were approximately 500 yards (460 m) apart, separated by a grassy area with a slight rise in the middle. Colonel Pedro Delgado later wrote that "the camping ground of His Excellency's selection was in all respects, against military rules. Any youngster would have done better."
Over the next several hours, two brief skirmishes occurred. Texians won the first, forcing a small group of dragoons and the Mexican artillery to withdraw. Mexican dragoons then forced the Texian cavalry to withdraw. In the melee, Rusk, on foot to reload his rifle, was almost captured by Mexican soldiers, but was rescued by newly arrived Texian volunteer Mirabeau B. Lamar. Over Houston's objections, many infantrymen rushed onto the field. As the Texian cavalry fell back, Lamar remained behind to rescue another Texian who had been thrown from his horse; Mexican officers "reportedly applauded" his bravery. Houston was irate that the infantry had disobeyed his orders and given Santa Anna a better estimate of their strength; the men were equally upset that Houston had not allowed a full battle.
Throughout the night, Mexican troops worked to fortify their camp, creating breastworks out of everything they could find, including saddles and brush. At 9 a.m. on April 21, Cos arrived with 540 reinforcements, bringing the Mexican force to approximately 1200-1500 men which outnumbered the Texian aggregate forces of approximately 800 men (official count entering battle was reported at 783). General Cos' men were mostly raw recruits rather than experienced soldiers, and they had marched steadily for more than 24 hours, with no rest and no food. As the morning wore on with no Texian attack, Mexican officers lowered their guard. By afternoon, Santa Anna had given permission for Cos' men to sleep; his own tired troops also took advantage of the time to rest, eat, and bathe.
Not long after Cos arrived with reinforcements, General Houston ordered Smith to destroy Vince's Bridge (located about 8 miles from the Texian encampment) to block the only road out of the Brassos and, thereby, prevent any possibility of escape by Santa Anna. General Sam Houston described how he arrayed the Texian forces in preparation of battle: "Colonel Edward Burleson was assigned the center. The second regiment, under the command of Colonel Sydney Sherman, formed the left wing of the army. The artillery, under the special command of Col. Geo. W. Hackley, inspector general, was placed on the right of the first regiment, and four companies under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Henry Millard, sustained the artillery on the right, and our cavalry, sixty-one in number and commanded by Colonel Mirabeau B. Lamar...placed on our extreme right, composed our line."
The Texian cavalry was first dispatched to the Mexican forces' far left and the artillery advanced through the tall grass to within 200 yards of the Mexican breastworks. . The Texian cannon fired at 4:30, beginning the battle of San Jacinto. After a single volley, Texians broke ranks and swarmed over the Mexican breastworks to engage in hand-to-hand combat. Mexican soldiers were taken by surprise. Santa Anna, Castrillón, and Almonte yelled often conflicting orders, attempting to organize their men into some form of defense. The Texian infantry forces advanced without halt until they had possession of the woodland and the Mexican breastwork; the right wing of Burleson's and the left wing of Millard's forces took possession of the breastwork. Within 18 minutes, Mexican soldiers abandoned their campsite and fled for their lives. The killing lasted for hours.
Many Mexican soldiers retreated through the marsh to Peggy Lake. Texian riflemen stationed themselves on the banks and shot at anything that moved. Many Texian officers, including Houston and Rusk, attempted to stop the slaughter, but they were unable to gain control of the men. Texians continued to chant "Remember the Alamo! Remember Goliad!" while frightened Mexican infantry yelled "Me no Alamo!" and begged for mercy to no avail. In what historian Davis called "one of the most one-sided victories in history", 650 Mexican soldiers were killed and 300 captured. Eleven Texians died, with 30 others, including Houston, wounded.
Although Santa Anna's troops had been thoroughly vanquished, they did not represent the bulk of the Mexican army in Texas. An additional 4,000 troops remained under the commands of Urrea and General Vicente Filisola. Texians had won the battle due to mistakes made by Santa Anna, and Houston was well aware that his troops would have little hope of repeating their victory against Urrea or Filisola. As darkness fell, a large group of prisoners was led into camp. Houston initially mistook the group for Mexican reinforcements and reportedly shouted out that all was lost.
Mexican retreat

A group of men are gathered under a large tree. One man lays on the ground under the trees, with his bare foot exposed. "Surrender of Santa Anna" by William Henry Huddle shows the Mexican president and general surrendering to a wounded Sam Houston, battle of San Jacinto
Santa Anna had escaped towards Vince's Bridge. Finding the bridge destroyed, he hid in the marsh and was captured the following day.[80] He was brought before Houston, who had been shot in the ankle and badly wounded. Texian soldiers gathered around, calling for the Mexican general's immediate execution. Bargaining for his life, Santa Anna suggested that he order the remaining Mexican troops to stay away. In a letter to Filisola, who was now the senior Mexican official in Texas, Santa Anna wrote that "yesterday evening [we] had an unfortunate encounter" and ordered his troops to retreat to Béxar and await further instructions.
Urrea urged Filisola to continue the campaign. He was confident that he could challenge the Texian troops. According to Hardin, "Santa Anna had presented Mexico with one military disaster; Filisola did not wish to risk another. Spring rains had ruined the ammunition and rendered the roads nearly impassable, with troops sinking to their knees in mud. The Mexican troops were soon out of food and began to fall ill from dysentery and other diseases. Their supply lines had broken down, leaving no hope of further reinforcements. Filisola later wrote that "Had the enemy met us under these cruel circumstances, on the only road that was left, no alternative remained but to die or surrender at discretion".
For several weeks after San Jacinto, Santa Anna continued to negotiate with Houston, Rusk, and then Burnet. Santa Anna suggested two treaties, a public version of promises made between the two countries, and a private version that included Santa Anna's personal agreements. The Treaties of Velasco required that all Mexican troops withdraw south of the Rio Grande and that all private property be respected and restored. Prisoners of war would be released unharmed and Santa Anna would be given immediate passage to Veracruz. He secretly promised to persuade the Mexican Congress to acknowledge the Republic of Texas and to recognize the Rio Grande as the border between the two countries.
When Urrea began marching south in mid-May, many families from San Patricio who had supported the Mexican army went with him. When Texian troops arrived in early June, they found only 20 families remaining. The area around San Patricio and Refugio suffered a "noticeable depopulation" in the Republic of Texas years. Although the treaty had specified that Urrea and Filisola would return any slaves their armies had sheltered, Urrea refused to comply. Many former slaves followed the army to Mexico, where they could be free. By late May, the Mexican troops had crossed the Nueces. Filisola fully expected that the defeat was temporary and that a second campaign would be launched to retake Texas.
</snip>

The Battle of San Jacinto – 1895 painting by Henry Arthur McArdle (1836–1908)
The Battle of San Jacinto (Spanish: Batalla de San Jacinto), fought on April 21, 1836, in present-day Harris County, Texas, was the decisive battle of the Texas Revolution. Led by General Sam Houston, the Texian Army engaged and defeated General Antonio López de Santa Anna's Mexican army in a fight that lasted just 18 minutes. A detailed, first-hand account of the battle was written by General Houston from Headquarters of the Texian Army, San Jacinto, on April 25, 1836.[3] Numerous secondary analyses and interpretations have followed, several of which are cited and discussed throughout this entry.
General Santa Anna, the President of Mexico, and General Martín Perfecto de Cos both escaped during the battle. Santa Anna was captured the next day on April 22 and Cos on April 24, 1836. After being held about three weeks as a prisoner of war, Santa Anna signed the peace treaty that dictated that the Mexican army leave the region, paving the way for the Republic of Texas to become an independent country. These treaties did not specifically recognize Texas as a sovereign nation, but stipulated that Santa Anna was to lobby for such recognition in Mexico City. Sam Houston became a national celebrity, and the Texans' rallying cries from events of the war, "Remember the Alamo!" and "Remember Goliad!" became etched into Texan history and legend.
<snip>
San Jacinto
The area along Buffalo Bayou had many thick oak groves, separated by marshes. This type of terrain was familiar to the Texians and quite alien to the Mexican soldiers. Houston's army, comprising 900 men, reached Lynch's Ferry mid-morning on April 20; Santa Anna's 700-man force arrived a few hours later. The Texians made camp in a wooded area along the bank of Buffalo Bayou; while the location provided good cover and helped hide their full strength, it also left the Texians no room for retreat. Over the protests of several of his officers, Santa Anna chose to make camp in a vulnerable location, a plain near the San Jacinto River, bordered by woods on one side, marsh and lake on another. The two camps were approximately 500 yards (460 m) apart, separated by a grassy area with a slight rise in the middle. Colonel Pedro Delgado later wrote that "the camping ground of His Excellency's selection was in all respects, against military rules. Any youngster would have done better."
Over the next several hours, two brief skirmishes occurred. Texians won the first, forcing a small group of dragoons and the Mexican artillery to withdraw. Mexican dragoons then forced the Texian cavalry to withdraw. In the melee, Rusk, on foot to reload his rifle, was almost captured by Mexican soldiers, but was rescued by newly arrived Texian volunteer Mirabeau B. Lamar. Over Houston's objections, many infantrymen rushed onto the field. As the Texian cavalry fell back, Lamar remained behind to rescue another Texian who had been thrown from his horse; Mexican officers "reportedly applauded" his bravery. Houston was irate that the infantry had disobeyed his orders and given Santa Anna a better estimate of their strength; the men were equally upset that Houston had not allowed a full battle.
Throughout the night, Mexican troops worked to fortify their camp, creating breastworks out of everything they could find, including saddles and brush. At 9 a.m. on April 21, Cos arrived with 540 reinforcements, bringing the Mexican force to approximately 1200-1500 men which outnumbered the Texian aggregate forces of approximately 800 men (official count entering battle was reported at 783). General Cos' men were mostly raw recruits rather than experienced soldiers, and they had marched steadily for more than 24 hours, with no rest and no food. As the morning wore on with no Texian attack, Mexican officers lowered their guard. By afternoon, Santa Anna had given permission for Cos' men to sleep; his own tired troops also took advantage of the time to rest, eat, and bathe.
Not long after Cos arrived with reinforcements, General Houston ordered Smith to destroy Vince's Bridge (located about 8 miles from the Texian encampment) to block the only road out of the Brassos and, thereby, prevent any possibility of escape by Santa Anna. General Sam Houston described how he arrayed the Texian forces in preparation of battle: "Colonel Edward Burleson was assigned the center. The second regiment, under the command of Colonel Sydney Sherman, formed the left wing of the army. The artillery, under the special command of Col. Geo. W. Hackley, inspector general, was placed on the right of the first regiment, and four companies under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Henry Millard, sustained the artillery on the right, and our cavalry, sixty-one in number and commanded by Colonel Mirabeau B. Lamar...placed on our extreme right, composed our line."
The Texian cavalry was first dispatched to the Mexican forces' far left and the artillery advanced through the tall grass to within 200 yards of the Mexican breastworks. . The Texian cannon fired at 4:30, beginning the battle of San Jacinto. After a single volley, Texians broke ranks and swarmed over the Mexican breastworks to engage in hand-to-hand combat. Mexican soldiers were taken by surprise. Santa Anna, Castrillón, and Almonte yelled often conflicting orders, attempting to organize their men into some form of defense. The Texian infantry forces advanced without halt until they had possession of the woodland and the Mexican breastwork; the right wing of Burleson's and the left wing of Millard's forces took possession of the breastwork. Within 18 minutes, Mexican soldiers abandoned their campsite and fled for their lives. The killing lasted for hours.
Many Mexican soldiers retreated through the marsh to Peggy Lake. Texian riflemen stationed themselves on the banks and shot at anything that moved. Many Texian officers, including Houston and Rusk, attempted to stop the slaughter, but they were unable to gain control of the men. Texians continued to chant "Remember the Alamo! Remember Goliad!" while frightened Mexican infantry yelled "Me no Alamo!" and begged for mercy to no avail. In what historian Davis called "one of the most one-sided victories in history", 650 Mexican soldiers were killed and 300 captured. Eleven Texians died, with 30 others, including Houston, wounded.
Although Santa Anna's troops had been thoroughly vanquished, they did not represent the bulk of the Mexican army in Texas. An additional 4,000 troops remained under the commands of Urrea and General Vicente Filisola. Texians had won the battle due to mistakes made by Santa Anna, and Houston was well aware that his troops would have little hope of repeating their victory against Urrea or Filisola. As darkness fell, a large group of prisoners was led into camp. Houston initially mistook the group for Mexican reinforcements and reportedly shouted out that all was lost.
Mexican retreat

A group of men are gathered under a large tree. One man lays on the ground under the trees, with his bare foot exposed. "Surrender of Santa Anna" by William Henry Huddle shows the Mexican president and general surrendering to a wounded Sam Houston, battle of San Jacinto
Santa Anna had escaped towards Vince's Bridge. Finding the bridge destroyed, he hid in the marsh and was captured the following day.[80] He was brought before Houston, who had been shot in the ankle and badly wounded. Texian soldiers gathered around, calling for the Mexican general's immediate execution. Bargaining for his life, Santa Anna suggested that he order the remaining Mexican troops to stay away. In a letter to Filisola, who was now the senior Mexican official in Texas, Santa Anna wrote that "yesterday evening [we] had an unfortunate encounter" and ordered his troops to retreat to Béxar and await further instructions.
Urrea urged Filisola to continue the campaign. He was confident that he could challenge the Texian troops. According to Hardin, "Santa Anna had presented Mexico with one military disaster; Filisola did not wish to risk another. Spring rains had ruined the ammunition and rendered the roads nearly impassable, with troops sinking to their knees in mud. The Mexican troops were soon out of food and began to fall ill from dysentery and other diseases. Their supply lines had broken down, leaving no hope of further reinforcements. Filisola later wrote that "Had the enemy met us under these cruel circumstances, on the only road that was left, no alternative remained but to die or surrender at discretion".
For several weeks after San Jacinto, Santa Anna continued to negotiate with Houston, Rusk, and then Burnet. Santa Anna suggested two treaties, a public version of promises made between the two countries, and a private version that included Santa Anna's personal agreements. The Treaties of Velasco required that all Mexican troops withdraw south of the Rio Grande and that all private property be respected and restored. Prisoners of war would be released unharmed and Santa Anna would be given immediate passage to Veracruz. He secretly promised to persuade the Mexican Congress to acknowledge the Republic of Texas and to recognize the Rio Grande as the border between the two countries.
When Urrea began marching south in mid-May, many families from San Patricio who had supported the Mexican army went with him. When Texian troops arrived in early June, they found only 20 families remaining. The area around San Patricio and Refugio suffered a "noticeable depopulation" in the Republic of Texas years. Although the treaty had specified that Urrea and Filisola would return any slaves their armies had sheltered, Urrea refused to comply. Many former slaves followed the army to Mexico, where they could be free. By late May, the Mexican troops had crossed the Nueces. Filisola fully expected that the defeat was temporary and that a second campaign would be launched to retake Texas.
</snip>
April 20, 2019

9 Years Ago Today; Deepwater Horizon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deepwater_Horizon

Deepwater Horizon was an ultra-deepwater, dynamically positioned, semi-submersible offshore drilling rig[8] owned by Transocean. Built in 2001 in South Korea by Hyundai Heavy Industries,[9] the rig was commissioned by R&B Falcon (a later asset of Transocean),[10] registered in Majuro, and leased to BP from 2001 until September 2013.[11] In September 2009, the rig drilled the deepest oil well in history at a vertical depth of 35,050 ft (10,683 m) and measured depth of 35,055 ft (10,685 m)[12] in the Tiber Oil Field at Keathley Canyon block 102, approximately 250 miles (400 km) southeast of Houston, in 4,132 feet (1,259 m) of water.
On 20 April 2010, while drilling at the Macondo Prospect, an uncontrollable blowout caused an explosion on the rig that killed 11 crewmen and ignited a fireball visible from 40 miles (64 km) away.[14] The fire was inextinguishable and, two days later, on 22 April, the Horizon sank, leaving the well gushing at the seabed and causing the largest oil spill in U.S. waters.
<snip>
Explosion and oil spill
At 9:45 P.M. CDT on 20 April 2010, during the final phases of drilling the exploratory well at Macondo, a geyser of seawater erupted from the marine riser onto the rig, shooting 240 ft (73 m) into the air. This was soon followed by the eruption of a slushy combination of drilling mud, methane gas, and water. The gas component of the slushy material quickly transitioned into a fully gaseous state and then ignited into a series of explosions and then a firestorm. An attempt was made to activate the blowout preventer, but it failed. The final defense to prevent an oil spill, a device known as a blind shear ram, was activated but failed to plug the well.
At the time of the explosion, there were 126 crew on board; seven were employees of BP, 79 of Transocean, there were also employees of various other companies involved in the operation of the rig, including Anadarko, Halliburton and M-I SWACO. Eleven workers were presumed killed in the initial explosion. The rig was evacuated, with injured workers airlifted to medical facilities. After approximately 36 hours, Deepwater Horizon sank on 22 April 2010. The remains of the rig were located resting on the seafloor approximately 5,000 ft (1,500 m) deep at that location, and about 1,300 ft (400 m) (quarter of a mile) northwest of the well.
The resultant oil spill continued until 15 July when it was closed by a cap. Relief wells were used to permanently seal the well, which was declared "effectively dead" on 19 September 2010.
Aftermath
Transocean received an early partial insurance settlement for total loss of the Deepwater Horizon of US $401 million around 5 May 2010. Financial analysts noted that the insurance recovery was likely to outweigh the value of the rig (although not necessarily its replacement value) and any liabilities – the latter estimated at up to US$200 million.
Litigation, ultimate roll call of damage, and the scope of final insurance recovery were all unknown as of June 2010, with analysts reporting that the aftermath was of unprecedented scale and complexity compared to previous disasters which themselves took many years to unfold and resolve. A July 2010 analysis by the Financial Times on the aftermath cited legal sources as saying that "at some point the scale of the litigation becomes so large that it really is novel", that "the situation is likely to be complicated further because the variety of probable cases means it will be hard to aggregate them into so-called class actions" and that there was "no way to put this in historical context because we have never faced anything like this before". As with the Exxon Valdez disaster, litigation was being discussed in terms of a 20-year timescale.
In January 2013, Transocean agreed to pay US$1.4 billion for violations of the US Clean Water Act. BP had earlier agreed to pay $2.4 billion but faced additional penalties that could range from $5 billion to $20 billion.[63] In September 2014, Halliburton agreed to settle a large percentage of legal claims against them by paying $1.1 billion into a trust by way of three installments over two years. On 4 September 2014, U.S. District Judge Carl Barbier ruled BP was guilty of gross negligence and willful misconduct under the Clean Water Act (CWA). He described BP's actions as "reckless," while he said Transocean's and Halliburton's actions were "negligent." He apportioned 67% of the blame for the spill to BP, 30% to Transocean, and 3% to Halliburton. BP issued a statement strongly disagreeing with the finding, and saying the court's decision would be appealed.
On 8 December 2014, The US Supreme Court rejected BP's legal challenge to a compensation deal over the 2010 Gulf of Mexico oil spill. The settlement agreement had no cap, but BP initially estimated that it would pay roughly $7.8bn (£6.1bn) to compensate victims.
</snip>

Deepwater Horizon was an ultra-deepwater, dynamically positioned, semi-submersible offshore drilling rig[8] owned by Transocean. Built in 2001 in South Korea by Hyundai Heavy Industries,[9] the rig was commissioned by R&B Falcon (a later asset of Transocean),[10] registered in Majuro, and leased to BP from 2001 until September 2013.[11] In September 2009, the rig drilled the deepest oil well in history at a vertical depth of 35,050 ft (10,683 m) and measured depth of 35,055 ft (10,685 m)[12] in the Tiber Oil Field at Keathley Canyon block 102, approximately 250 miles (400 km) southeast of Houston, in 4,132 feet (1,259 m) of water.
On 20 April 2010, while drilling at the Macondo Prospect, an uncontrollable blowout caused an explosion on the rig that killed 11 crewmen and ignited a fireball visible from 40 miles (64 km) away.[14] The fire was inextinguishable and, two days later, on 22 April, the Horizon sank, leaving the well gushing at the seabed and causing the largest oil spill in U.S. waters.
<snip>
Explosion and oil spill
At 9:45 P.M. CDT on 20 April 2010, during the final phases of drilling the exploratory well at Macondo, a geyser of seawater erupted from the marine riser onto the rig, shooting 240 ft (73 m) into the air. This was soon followed by the eruption of a slushy combination of drilling mud, methane gas, and water. The gas component of the slushy material quickly transitioned into a fully gaseous state and then ignited into a series of explosions and then a firestorm. An attempt was made to activate the blowout preventer, but it failed. The final defense to prevent an oil spill, a device known as a blind shear ram, was activated but failed to plug the well.
At the time of the explosion, there were 126 crew on board; seven were employees of BP, 79 of Transocean, there were also employees of various other companies involved in the operation of the rig, including Anadarko, Halliburton and M-I SWACO. Eleven workers were presumed killed in the initial explosion. The rig was evacuated, with injured workers airlifted to medical facilities. After approximately 36 hours, Deepwater Horizon sank on 22 April 2010. The remains of the rig were located resting on the seafloor approximately 5,000 ft (1,500 m) deep at that location, and about 1,300 ft (400 m) (quarter of a mile) northwest of the well.
The resultant oil spill continued until 15 July when it was closed by a cap. Relief wells were used to permanently seal the well, which was declared "effectively dead" on 19 September 2010.
Aftermath
Transocean received an early partial insurance settlement for total loss of the Deepwater Horizon of US $401 million around 5 May 2010. Financial analysts noted that the insurance recovery was likely to outweigh the value of the rig (although not necessarily its replacement value) and any liabilities – the latter estimated at up to US$200 million.
Litigation, ultimate roll call of damage, and the scope of final insurance recovery were all unknown as of June 2010, with analysts reporting that the aftermath was of unprecedented scale and complexity compared to previous disasters which themselves took many years to unfold and resolve. A July 2010 analysis by the Financial Times on the aftermath cited legal sources as saying that "at some point the scale of the litigation becomes so large that it really is novel", that "the situation is likely to be complicated further because the variety of probable cases means it will be hard to aggregate them into so-called class actions" and that there was "no way to put this in historical context because we have never faced anything like this before". As with the Exxon Valdez disaster, litigation was being discussed in terms of a 20-year timescale.
In January 2013, Transocean agreed to pay US$1.4 billion for violations of the US Clean Water Act. BP had earlier agreed to pay $2.4 billion but faced additional penalties that could range from $5 billion to $20 billion.[63] In September 2014, Halliburton agreed to settle a large percentage of legal claims against them by paying $1.1 billion into a trust by way of three installments over two years. On 4 September 2014, U.S. District Judge Carl Barbier ruled BP was guilty of gross negligence and willful misconduct under the Clean Water Act (CWA). He described BP's actions as "reckless," while he said Transocean's and Halliburton's actions were "negligent." He apportioned 67% of the blame for the spill to BP, 30% to Transocean, and 3% to Halliburton. BP issued a statement strongly disagreeing with the finding, and saying the court's decision would be appealed.
On 8 December 2014, The US Supreme Court rejected BP's legal challenge to a compensation deal over the 2010 Gulf of Mexico oil spill. The settlement agreement had no cap, but BP initially estimated that it would pay roughly $7.8bn (£6.1bn) to compensate victims.
</snip>
April 20, 2019
Jesus, and this is *still* happening today... "Doomed to repeat..."
20 Years Ago Today; Massacre at Columbine
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Columbine_High_School_massacre

Eric Harris (left) and Dylan Klebold (right) recorded on the high school's surveillance cameras in the cafeteria, 11 minutes before their suicides
The Columbine High School massacre was a school shooting that occurred on April 20, 1999, at Columbine High School in Columbine, Colorado, United States. The perpetrators, twelfth grade (senior) students Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold, murdered 12 students and one teacher. Ten students were killed in the library, where the pair subsequently committed suicide. At the time, it was the deadliest shooting at a high school in United States history. The crime has inspired several copycats, and "Columbine" has become a byword for a school shooting.
The two perpetrators injured 21 additional people with gunshots and also exchanged gunfire with the police. Another three people were injured trying to escape the school. In addition to the shootings, the attack involved several homemade bombs. The largest of these were placed in the cafeteria; car bombs were also placed in the parking lot and at another location that was intended to divert first responders.
The motive remains unclear, but the pair planned the crime for about a year and wished for the massacre to rival the Oklahoma City bombing and cause the most deaths in United States history. USA Today referred to the attack as "planned as a grand, if badly implemented, terrorist bombing."
The police were slow to enter the school, and they were heavily criticized for not intervening during the shooting. The incident resulted in the introduction of the Immediate Action Rapid Deployment tactic, which is used in situations where an active shooter is trying to kill people rather than take hostages. Columbine also resulted in an increased emphasis on school security with zero tolerance policies. Debates were sparked over gun control laws and gun culture, high school cliques, subcultures, and bullying. Also discussed were the moral panic over goths, social outcasts, the use of pharmaceutical antidepressants by teenagers, teenage Internet use and violence in video games.
</snip>

Eric Harris (left) and Dylan Klebold (right) recorded on the high school's surveillance cameras in the cafeteria, 11 minutes before their suicides
The Columbine High School massacre was a school shooting that occurred on April 20, 1999, at Columbine High School in Columbine, Colorado, United States. The perpetrators, twelfth grade (senior) students Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold, murdered 12 students and one teacher. Ten students were killed in the library, where the pair subsequently committed suicide. At the time, it was the deadliest shooting at a high school in United States history. The crime has inspired several copycats, and "Columbine" has become a byword for a school shooting.
The two perpetrators injured 21 additional people with gunshots and also exchanged gunfire with the police. Another three people were injured trying to escape the school. In addition to the shootings, the attack involved several homemade bombs. The largest of these were placed in the cafeteria; car bombs were also placed in the parking lot and at another location that was intended to divert first responders.
The motive remains unclear, but the pair planned the crime for about a year and wished for the massacre to rival the Oklahoma City bombing and cause the most deaths in United States history. USA Today referred to the attack as "planned as a grand, if badly implemented, terrorist bombing."
The police were slow to enter the school, and they were heavily criticized for not intervening during the shooting. The incident resulted in the introduction of the Immediate Action Rapid Deployment tactic, which is used in situations where an active shooter is trying to kill people rather than take hostages. Columbine also resulted in an increased emphasis on school security with zero tolerance policies. Debates were sparked over gun control laws and gun culture, high school cliques, subcultures, and bullying. Also discussed were the moral panic over goths, social outcasts, the use of pharmaceutical antidepressants by teenagers, teenage Internet use and violence in video games.
</snip>
Jesus, and this is *still* happening today... "Doomed to repeat..."
April 19, 2019

24 Years Ago Today; Terror in OKC
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oklahoma_City_bombing

The Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building two days after the bombing, viewed from across the adjacent parking lot
The Oklahoma City bombing was a domestic terrorist truck bombing on the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in downtown Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States on April 19, 1995. Perpetrated by Timothy McVeigh and Terry Nichols, the bombing happened at 9:02 am and killed at least 168 people, injured more than 680 others, and destroyed one-third of the building. The blast destroyed or damaged 324 other buildings within a 16-block radius, shattered glass in 258 nearby buildings, and destroyed or burned 86 cars, causing an estimated $652 million worth of damage. Extensive rescue efforts were undertaken by local, state, federal, and worldwide agencies in the wake of the bombing, and substantial donations were received from across the country. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) activated 11 of its Urban Search and Rescue Task Forces, consisting of 665 rescue workers who assisted in rescue and recovery operations. Until the September 11, 2001 attacks, the Oklahoma City bombing was the deadliest terrorist attack in the history of the United States, and remains the deadliest incident of domestic terrorism in the country's history.
Within 90 minutes of the explosion, McVeigh was stopped by Oklahoma Highway Patrolman Charlie Hanger for driving without a license plate and arrested for illegal weapons possession. Forensic evidence quickly linked McVeigh and Nichols to the attack; Nichols was arrested, and within days, both were charged. Michael and Lori Fortier were later identified as accomplices. McVeigh, a veteran of the Gulf War and a U.S. militia movement sympathizer, had detonated a Ryder rental truck full of explosives parked in front of the building. His co-conspirator, Nichols, had assisted with the bomb's preparation. Motivated by his dislike for the U.S. federal government and unhappy about its handling of the Ruby Ridge incident in 1992 and the Waco siege in 1993, McVeigh timed his attack to coincide with the second anniversary of the deadly fire that ended the siege at the Branch Davidian compound in Waco, Texas.
The official investigation, known as "OKBOMB", saw FBI agents conduct 28,000 interviews, amass 3.5 short tons (3,200 kg) of evidence, and collected nearly one billion pieces of information. The bombers were tried and convicted in 1997. McVeigh was executed by lethal injection on June 11, 2001, and Nichols was sentenced to life in prison in 2004. Michael and Lori Fortier testified against McVeigh and Nichols; Michael was sentenced to 12 years in prison for failing to warn the United States government, and Lori received immunity from prosecution in exchange for her testimony.
As a result of the bombing, the U.S. Congress passed the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996, which tightened the standards for habeas corpus in the United States, as well as legislation designed to increase the protection around federal buildings to deter future terrorist attacks. On April 19, 2000, the Oklahoma City National Memorial was dedicated on the site of the Murrah Federal Building, commemorating the victims of the bombing. Remembrance services are held every year on April 19, at the time of the explosion.
<snip>
Bombing

Map showing the layout of downtown Oklahoma City near the bombed building. The map uses simple shapes to identify some notable nearby buildings and roads. A large circle covers half the map, illustrating the extent of damage from the bomb. A red path shows the path McVeigh took to get to the building with the Ryder truck, and a blue line shows his escape on foot.
McVeigh's original plan had been to detonate the bomb at 11:00 am, but at dawn on April 19, 1995, he decided instead to destroy the building at 9:00 am. As he drove toward the Murrah Federal Building in the Ryder truck, McVeigh carried with him an envelope containing pages from The Turner Diaries – a fictional account of white supremacists who ignite a revolution by blowing up the FBI headquarters at 9:15 one morning using a truck bomb. McVeigh wore a printed T-shirt with the motto of the Commonwealth of Virginia, Sic semper tyrannis ("Thus always to tyrants", according to legend what Brutus said as he assassinated Julius Caesar, also shouted by John Wilkes Booth immediately after the assassination of Abraham Lincoln) and "The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants" (from Thomas Jefferson). He also carried an envelope full of revolutionary materials that included a bumper sticker with the Thomas Jefferson slogan, "When the government fears the people, there is liberty. When the people fear the government, there is tyranny." Underneath, McVeigh had written, "Maybe now, there will be liberty!" with a hand-copied quote by John Locke asserting that a man has a right to kill someone who takes away his liberty.
McVeigh entered Oklahoma City at 8:50 am. At 8:57 am, the Regency Towers Apartments' lobby security camera that had recorded Nichols's pickup truck three days earlier recorded the Ryder truck heading towards the Murrah Federal Building. At the same moment, McVeigh lit the five-minute fuse. Three minutes later, still a block away, he lit the two-minute fuse. He parked the Ryder truck in a drop-off zone situated under the building's day-care center, exited and locked the truck, and as he headed to his getaway vehicle, dropped the keys to the truck a few blocks away.

An overhead view shows the Alfred P. Murrah building, half of it destroyed from the bomb's blast. Near the building are various rescue vehicles and cranes. Some damage is visible to nearby buildings.
At 9:02 a.m. (14:02 UTC), the Ryder truck, containing over 4,800 pounds (2,200 kg) of ammonium nitrate fertilizer, nitromethane, and diesel fuel mixture, detonated in front of the north side of the nine-story Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building. 168 people were killed and hundreds more injured. One third of the building was destroyed by the explosion, which created a 30-foot-wide (9.1 m), 8-foot-deep (2.4 m) crater on NW 5th Street next to the building. The blast destroyed or damaged 324 buildings within a 4-block radius, and shattered glass in 258 nearby buildings. The broken glass alone accounted for 5% of the death total and 69% of the injuries outside the Murrah Federal Building. The blast destroyed or burned 86 cars around the site. The destruction of the buildings left several hundred people homeless and shut down a number of offices in downtown Oklahoma City. The explosion was estimated to have caused at least $652 million worth of damage.
The effects of the blast were equivalent to over 5,000 pounds (2,300 kg) of TNT, and could be heard and felt up to 55 miles (89 km) away.[68] Seismometers at the Omniplex Science Museum in Oklahoma City, 4.3 miles (6.9 km) away, and in Norman, Oklahoma, 16.1 miles (25.9 km) away, recorded the blast as measuring approximately 3.0 on the Richter magnitude scale.
<snip>
Casualties
An estimated 646 people were inside the building when the bomb exploded. By the end of the day, 14 adults and 6 children were confirmed dead, and over 100 injured. The toll eventually reached 168 confirmed dead, not including an unmatched left leg that could have belonged to an unidentified 169th victim or could have belonged to any one of eight victims who had been buried without a left leg. Most of the deaths resulted from the collapse of the building, rather than the bomb blast itself. Those killed included 163 who were in the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building, one person in the Athenian Building, one woman in a parking lot across the street, a man and woman in the Oklahoma Water Resources building, and a rescue worker struck on the head by debris.
The victims, including three pregnant women, ranged in age from three months to 73 years. Of the dead, 108 worked for the Federal government: Drug Enforcement Administration (5); Secret Service (6); Department of Housing and Urban Development (35); Department of Agriculture (7); Customs Office (2); Department of Transportation/Federal Highway (11); General Services Administration (2); and the Social Security Administration (40).[96] Eight of the federal government victims were federal law enforcement agents. Of those law enforcement agents four were members of the U.S. Secret Service, two were members of the U.S. Customs Service, one was a member of the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, and one was a member of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Six of the victims were U.S. military personnel; two members of the U.S. Army, two members of the U.S. Air Force, two members of the U.S. Marine Corps. The rest of the victims were civilians, including 19 children, of whom 15 were in the America's Kids Day Care Center. The bodies of the 168 victims were identified at a temporary morgue set up at the scene. A team of 24 identified the victims using full-body X-rays, dental examinations, fingerprinting, blood tests, and DNA testing. More than 680 people were injured. The majority of the injuries were abrasions, severe burns, and bone fractures.
McVeigh's later response to the range of casualties was: "I didn't define the rules of engagement in this conflict. The rules, if not written down, are defined by the aggressor. It was brutal, no holds barred. Women and kids were killed at Waco and Ruby Ridge. You put back in [the government's] faces exactly what they're giving out.
<snip>
Oklahoma City National Memorial

Panoramic view of the memorial, as seen from the base of the reflecting pool. From left to right are the memorial chairs, Gate of Time and Reflecting Pool, the Survivor Tree, and the Journal Record Building.
For two years after the bombing the only memorials to the victims were plush toys, crucifixes, letters, and other personal items left by thousands of people at a security fence surrounding the site of the building. Many suggestions for suitable memorials were sent to Oklahoma City, but an official memorial planning committee was not set up until early 1996, when the Murrah Federal Building Memorial Task Force, composed of 350 members, was set up to formulate plans for a memorial to commemorate the victims of the bombing. On July 1, 1997 the winning design was chosen unanimously by a 15-member panel from 624 submissions. The memorial was designed at a cost of $29 million, which was raised by public and private funds. The national memorial is part of the National Park System as an affiliated area and was designed by Oklahoma City architects Hans and Torrey Butzer and Sven Berg. It was dedicated by President Clinton on April 19, 2000, exactly five years after the bombing. Within the first year, it had 700,000 visitors.
The memorial includes a reflecting pool flanked by two large gates, one inscribed with the time 9:01, the other with 9:03, the pool representing the moment of the blast. On the south end of the memorial is a field of symbolic bronze and stone chairs – one for each person lost, arranged according to what floor of the building they were on. The chairs represent the empty chairs at the dinner tables of the victims' families. The seats of the children killed are smaller than those of the adults lost. On the opposite side is the "survivor tree", part of the building's original landscaping that survived the blast and fires that followed it. The memorial left part of the foundation of the building intact, allowing visitors to see the scale of the destruction. Part of the chain link fence put in place around the site of the blast, which had attracted over 800,000 personal items of commemoration later collected by the Oklahoma City Memorial Foundation, is now on the western edge of the memorial. North of the memorial is the Journal Record Building, which now houses the Oklahoma City National Memorial Museum, an affiliate of the National Park Service. The building also contains the National Memorial Institute for the Prevention of Terrorism, a law enforcement training center.
</snip>

The Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building two days after the bombing, viewed from across the adjacent parking lot
The Oklahoma City bombing was a domestic terrorist truck bombing on the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in downtown Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States on April 19, 1995. Perpetrated by Timothy McVeigh and Terry Nichols, the bombing happened at 9:02 am and killed at least 168 people, injured more than 680 others, and destroyed one-third of the building. The blast destroyed or damaged 324 other buildings within a 16-block radius, shattered glass in 258 nearby buildings, and destroyed or burned 86 cars, causing an estimated $652 million worth of damage. Extensive rescue efforts were undertaken by local, state, federal, and worldwide agencies in the wake of the bombing, and substantial donations were received from across the country. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) activated 11 of its Urban Search and Rescue Task Forces, consisting of 665 rescue workers who assisted in rescue and recovery operations. Until the September 11, 2001 attacks, the Oklahoma City bombing was the deadliest terrorist attack in the history of the United States, and remains the deadliest incident of domestic terrorism in the country's history.
Within 90 minutes of the explosion, McVeigh was stopped by Oklahoma Highway Patrolman Charlie Hanger for driving without a license plate and arrested for illegal weapons possession. Forensic evidence quickly linked McVeigh and Nichols to the attack; Nichols was arrested, and within days, both were charged. Michael and Lori Fortier were later identified as accomplices. McVeigh, a veteran of the Gulf War and a U.S. militia movement sympathizer, had detonated a Ryder rental truck full of explosives parked in front of the building. His co-conspirator, Nichols, had assisted with the bomb's preparation. Motivated by his dislike for the U.S. federal government and unhappy about its handling of the Ruby Ridge incident in 1992 and the Waco siege in 1993, McVeigh timed his attack to coincide with the second anniversary of the deadly fire that ended the siege at the Branch Davidian compound in Waco, Texas.
The official investigation, known as "OKBOMB", saw FBI agents conduct 28,000 interviews, amass 3.5 short tons (3,200 kg) of evidence, and collected nearly one billion pieces of information. The bombers were tried and convicted in 1997. McVeigh was executed by lethal injection on June 11, 2001, and Nichols was sentenced to life in prison in 2004. Michael and Lori Fortier testified against McVeigh and Nichols; Michael was sentenced to 12 years in prison for failing to warn the United States government, and Lori received immunity from prosecution in exchange for her testimony.
As a result of the bombing, the U.S. Congress passed the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act of 1996, which tightened the standards for habeas corpus in the United States, as well as legislation designed to increase the protection around federal buildings to deter future terrorist attacks. On April 19, 2000, the Oklahoma City National Memorial was dedicated on the site of the Murrah Federal Building, commemorating the victims of the bombing. Remembrance services are held every year on April 19, at the time of the explosion.
<snip>
Bombing

Map showing the layout of downtown Oklahoma City near the bombed building. The map uses simple shapes to identify some notable nearby buildings and roads. A large circle covers half the map, illustrating the extent of damage from the bomb. A red path shows the path McVeigh took to get to the building with the Ryder truck, and a blue line shows his escape on foot.
McVeigh's original plan had been to detonate the bomb at 11:00 am, but at dawn on April 19, 1995, he decided instead to destroy the building at 9:00 am. As he drove toward the Murrah Federal Building in the Ryder truck, McVeigh carried with him an envelope containing pages from The Turner Diaries – a fictional account of white supremacists who ignite a revolution by blowing up the FBI headquarters at 9:15 one morning using a truck bomb. McVeigh wore a printed T-shirt with the motto of the Commonwealth of Virginia, Sic semper tyrannis ("Thus always to tyrants", according to legend what Brutus said as he assassinated Julius Caesar, also shouted by John Wilkes Booth immediately after the assassination of Abraham Lincoln) and "The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants" (from Thomas Jefferson). He also carried an envelope full of revolutionary materials that included a bumper sticker with the Thomas Jefferson slogan, "When the government fears the people, there is liberty. When the people fear the government, there is tyranny." Underneath, McVeigh had written, "Maybe now, there will be liberty!" with a hand-copied quote by John Locke asserting that a man has a right to kill someone who takes away his liberty.
McVeigh entered Oklahoma City at 8:50 am. At 8:57 am, the Regency Towers Apartments' lobby security camera that had recorded Nichols's pickup truck three days earlier recorded the Ryder truck heading towards the Murrah Federal Building. At the same moment, McVeigh lit the five-minute fuse. Three minutes later, still a block away, he lit the two-minute fuse. He parked the Ryder truck in a drop-off zone situated under the building's day-care center, exited and locked the truck, and as he headed to his getaway vehicle, dropped the keys to the truck a few blocks away.

An overhead view shows the Alfred P. Murrah building, half of it destroyed from the bomb's blast. Near the building are various rescue vehicles and cranes. Some damage is visible to nearby buildings.
At 9:02 a.m. (14:02 UTC), the Ryder truck, containing over 4,800 pounds (2,200 kg) of ammonium nitrate fertilizer, nitromethane, and diesel fuel mixture, detonated in front of the north side of the nine-story Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building. 168 people were killed and hundreds more injured. One third of the building was destroyed by the explosion, which created a 30-foot-wide (9.1 m), 8-foot-deep (2.4 m) crater on NW 5th Street next to the building. The blast destroyed or damaged 324 buildings within a 4-block radius, and shattered glass in 258 nearby buildings. The broken glass alone accounted for 5% of the death total and 69% of the injuries outside the Murrah Federal Building. The blast destroyed or burned 86 cars around the site. The destruction of the buildings left several hundred people homeless and shut down a number of offices in downtown Oklahoma City. The explosion was estimated to have caused at least $652 million worth of damage.
The effects of the blast were equivalent to over 5,000 pounds (2,300 kg) of TNT, and could be heard and felt up to 55 miles (89 km) away.[68] Seismometers at the Omniplex Science Museum in Oklahoma City, 4.3 miles (6.9 km) away, and in Norman, Oklahoma, 16.1 miles (25.9 km) away, recorded the blast as measuring approximately 3.0 on the Richter magnitude scale.
<snip>
Casualties
An estimated 646 people were inside the building when the bomb exploded. By the end of the day, 14 adults and 6 children were confirmed dead, and over 100 injured. The toll eventually reached 168 confirmed dead, not including an unmatched left leg that could have belonged to an unidentified 169th victim or could have belonged to any one of eight victims who had been buried without a left leg. Most of the deaths resulted from the collapse of the building, rather than the bomb blast itself. Those killed included 163 who were in the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building, one person in the Athenian Building, one woman in a parking lot across the street, a man and woman in the Oklahoma Water Resources building, and a rescue worker struck on the head by debris.
The victims, including three pregnant women, ranged in age from three months to 73 years. Of the dead, 108 worked for the Federal government: Drug Enforcement Administration (5); Secret Service (6); Department of Housing and Urban Development (35); Department of Agriculture (7); Customs Office (2); Department of Transportation/Federal Highway (11); General Services Administration (2); and the Social Security Administration (40).[96] Eight of the federal government victims were federal law enforcement agents. Of those law enforcement agents four were members of the U.S. Secret Service, two were members of the U.S. Customs Service, one was a member of the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, and one was a member of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. Six of the victims were U.S. military personnel; two members of the U.S. Army, two members of the U.S. Air Force, two members of the U.S. Marine Corps. The rest of the victims were civilians, including 19 children, of whom 15 were in the America's Kids Day Care Center. The bodies of the 168 victims were identified at a temporary morgue set up at the scene. A team of 24 identified the victims using full-body X-rays, dental examinations, fingerprinting, blood tests, and DNA testing. More than 680 people were injured. The majority of the injuries were abrasions, severe burns, and bone fractures.
McVeigh's later response to the range of casualties was: "I didn't define the rules of engagement in this conflict. The rules, if not written down, are defined by the aggressor. It was brutal, no holds barred. Women and kids were killed at Waco and Ruby Ridge. You put back in [the government's] faces exactly what they're giving out.
<snip>
Oklahoma City National Memorial

Panoramic view of the memorial, as seen from the base of the reflecting pool. From left to right are the memorial chairs, Gate of Time and Reflecting Pool, the Survivor Tree, and the Journal Record Building.
For two years after the bombing the only memorials to the victims were plush toys, crucifixes, letters, and other personal items left by thousands of people at a security fence surrounding the site of the building. Many suggestions for suitable memorials were sent to Oklahoma City, but an official memorial planning committee was not set up until early 1996, when the Murrah Federal Building Memorial Task Force, composed of 350 members, was set up to formulate plans for a memorial to commemorate the victims of the bombing. On July 1, 1997 the winning design was chosen unanimously by a 15-member panel from 624 submissions. The memorial was designed at a cost of $29 million, which was raised by public and private funds. The national memorial is part of the National Park System as an affiliated area and was designed by Oklahoma City architects Hans and Torrey Butzer and Sven Berg. It was dedicated by President Clinton on April 19, 2000, exactly five years after the bombing. Within the first year, it had 700,000 visitors.
The memorial includes a reflecting pool flanked by two large gates, one inscribed with the time 9:01, the other with 9:03, the pool representing the moment of the blast. On the south end of the memorial is a field of symbolic bronze and stone chairs – one for each person lost, arranged according to what floor of the building they were on. The chairs represent the empty chairs at the dinner tables of the victims' families. The seats of the children killed are smaller than those of the adults lost. On the opposite side is the "survivor tree", part of the building's original landscaping that survived the blast and fires that followed it. The memorial left part of the foundation of the building intact, allowing visitors to see the scale of the destruction. Part of the chain link fence put in place around the site of the blast, which had attracted over 800,000 personal items of commemoration later collected by the Oklahoma City Memorial Foundation, is now on the western edge of the memorial. North of the memorial is the Journal Record Building, which now houses the Oklahoma City National Memorial Museum, an affiliate of the National Park Service. The building also contains the National Memorial Institute for the Prevention of Terrorism, a law enforcement training center.
</snip>
April 19, 2019
It's almost hard to remember a world without the Simpsons...
32 Years Ago Today; Meet the Simpsons!
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Good_Night_(The_Simpsons)

The entire Simpson family in Homer and Marge's bed during the final segment of the short
"Good Night" (also known as "Good Night Simpsons" is the first of forty-eight Simpsons shorts that appeared on the variety show The Tracey Ullman Show. It originally aired on the Fox network in the United States on April 19, 1987, during the third episode of The Tracey Ullman Show and marks the first appearance of the Simpson family — Homer, Marge, Bart, Lisa, and Maggie — on television. After three seasons on Tracey Ullman, the shorts would be adapted into the animated show The Simpsons. "Good Night" has since been aired on the show in the episode "The Simpsons 138th Episode Spectacular" (in its entirety), along with several other Ullman shorts, and is one of the few shorts to ever be released on DVD, being included in the Season 1 DVD set.
is the first of forty-eight Simpsons shorts that appeared on the variety show The Tracey Ullman Show. It originally aired on the Fox network in the United States on April 19, 1987, during the third episode of The Tracey Ullman Show and marks the first appearance of the Simpson family — Homer, Marge, Bart, Lisa, and Maggie — on television. After three seasons on Tracey Ullman, the shorts would be adapted into the animated show The Simpsons. "Good Night" has since been aired on the show in the episode "The Simpsons 138th Episode Spectacular" (in its entirety), along with several other Ullman shorts, and is one of the few shorts to ever be released on DVD, being included in the Season 1 DVD set.
Plot
Homer and Marge say goodnight to their children, but all does not go according to plan. Bart tries to ask about the mind, but is left contemplating it as he does not get a proper answer. Lisa fears that bed bugs will eat her after hearing Marge say "Don't let the bed bugs bite". Maggie is terrified by the lyrics of "Rock-a-bye Baby". Ultimately, all of the three children decide to sleep in the parents' bed.
Origins
Groening first conceived of the Simpsons in the lobby of James L. Brooks' office. He had been called in to pitch a series of animated shorts, and had intended to present his Life in Hell series. When he realized that animating Life in Hell would require him to rescind publication rights for his life's work, Groening decided to go in another direction. He hurriedly sketched out his version of a dysfunctional family, and named the characters after his own family. Bart was modeled after Groening's older brother, Mark, but given a different name which was chosen as an anagram of "brat."
This short was written and storyboarded by Groening. The family was crudely drawn, because Groening had submitted basic sketches to the animators, assuming they would clean them up; instead they just traced over his drawings. The animation was produced at Klasky Csupo, with Wesley Archer, David Silverman, and Bill Kopp being animators.
Despite later making the decision for Maggie to not speak throughout the show's run, Maggie does say the words 'good night'. While Yeardley Smith does Maggie's babbling in the show, her speaking bits in this short were done by Liz Georges. The Simpsons Archive suggests that Gabor Csupo did the pacifier sucking noises, as opposed to Matt Groening who did the role later. At this point in time, the characters were very different from how they would be in the first season of The Simpsons and beyond. In addition to this, Homer was smarter than portrayed later and spoke in a Walter Matthau-style voice. Lisa misbehaved as much as Bart.
<snip>
Critical reception
FilmThreat says "This dark nursery rhyme is funny and disturbing. Homer’s voice is totally off the wall, nothing like it stands today, and it’s interesting to see how far they’ve come since these early forays into animation". Todd Doogan of The Digital Bits was sad that "only [one] of the original Tracey Ullman Show shorts" was featured on the first season DVD". He added, "Still, the one you gets perfectly illustrates just how far the show has come". DVD.net describes it as "The Simpsons as some of you may never have seen before, drawn by the hand of Matt Groening himself and looking a little worse for wear." DVD Movie Guide says, "I’ve seen a few additional Ullman shorts and think they’re nearly unwatchable, so I can’t say I miss them, at least not for their entertainment value. However, they’d make a nice historical addition, so it’s too bad we only get this single clip. The first one ever aired, “Good Night Simpsons” runs for 115 unfunny seconds." The Digital Fix says the short extra on the DVD "showcases the superb sense of humour that has made The Simpsons what it is today", and that "the picture quality is quite breathtaking (considering the age of these shorts) while the sound is standard DD2.0 Stereo". It adds that "it is a teaser for something we will supposedly never see (all 48 shorts on DVD)" and wishes they had chosen a short that hadn't been featured in a future episode (The 138th Episode Spectacular), and therefore released on the Season 7 Box set. Planet Simpson says "the drawing and animation were blatantly crude, thick-lined, and primary-colored" and that "the vignettes were far too short for anything as sophisticated as 'character development'". It adds that the "central gag [of] kids finding ironic horror in bedtime platitudes" was very simplistic, and doubts many people even watched the airing of the short. However, the book explains the significance of Good Night as "the first baby steps of an institution that would become one of the most-watched TV shows on earth and the most influential cultural enterprise of its time".

The entire Simpson family in Homer and Marge's bed during the final segment of the short
"Good Night" (also known as "Good Night Simpsons"
Plot
Homer and Marge say goodnight to their children, but all does not go according to plan. Bart tries to ask about the mind, but is left contemplating it as he does not get a proper answer. Lisa fears that bed bugs will eat her after hearing Marge say "Don't let the bed bugs bite". Maggie is terrified by the lyrics of "Rock-a-bye Baby". Ultimately, all of the three children decide to sleep in the parents' bed.
Origins
Groening first conceived of the Simpsons in the lobby of James L. Brooks' office. He had been called in to pitch a series of animated shorts, and had intended to present his Life in Hell series. When he realized that animating Life in Hell would require him to rescind publication rights for his life's work, Groening decided to go in another direction. He hurriedly sketched out his version of a dysfunctional family, and named the characters after his own family. Bart was modeled after Groening's older brother, Mark, but given a different name which was chosen as an anagram of "brat."
This short was written and storyboarded by Groening. The family was crudely drawn, because Groening had submitted basic sketches to the animators, assuming they would clean them up; instead they just traced over his drawings. The animation was produced at Klasky Csupo, with Wesley Archer, David Silverman, and Bill Kopp being animators.
Despite later making the decision for Maggie to not speak throughout the show's run, Maggie does say the words 'good night'. While Yeardley Smith does Maggie's babbling in the show, her speaking bits in this short were done by Liz Georges. The Simpsons Archive suggests that Gabor Csupo did the pacifier sucking noises, as opposed to Matt Groening who did the role later. At this point in time, the characters were very different from how they would be in the first season of The Simpsons and beyond. In addition to this, Homer was smarter than portrayed later and spoke in a Walter Matthau-style voice. Lisa misbehaved as much as Bart.
<snip>
Critical reception
FilmThreat says "This dark nursery rhyme is funny and disturbing. Homer’s voice is totally off the wall, nothing like it stands today, and it’s interesting to see how far they’ve come since these early forays into animation". Todd Doogan of The Digital Bits was sad that "only [one] of the original Tracey Ullman Show shorts" was featured on the first season DVD". He added, "Still, the one you gets perfectly illustrates just how far the show has come". DVD.net describes it as "The Simpsons as some of you may never have seen before, drawn by the hand of Matt Groening himself and looking a little worse for wear." DVD Movie Guide says, "I’ve seen a few additional Ullman shorts and think they’re nearly unwatchable, so I can’t say I miss them, at least not for their entertainment value. However, they’d make a nice historical addition, so it’s too bad we only get this single clip. The first one ever aired, “Good Night Simpsons” runs for 115 unfunny seconds." The Digital Fix says the short extra on the DVD "showcases the superb sense of humour that has made The Simpsons what it is today", and that "the picture quality is quite breathtaking (considering the age of these shorts) while the sound is standard DD2.0 Stereo". It adds that "it is a teaser for something we will supposedly never see (all 48 shorts on DVD)" and wishes they had chosen a short that hadn't been featured in a future episode (The 138th Episode Spectacular), and therefore released on the Season 7 Box set. Planet Simpson says "the drawing and animation were blatantly crude, thick-lined, and primary-colored" and that "the vignettes were far too short for anything as sophisticated as 'character development'". It adds that the "central gag [of] kids finding ironic horror in bedtime platitudes" was very simplistic, and doubts many people even watched the airing of the short. However, the book explains the significance of Good Night as "the first baby steps of an institution that would become one of the most-watched TV shows on earth and the most influential cultural enterprise of its time".
It's almost hard to remember a world without the Simpsons...
April 19, 2019


30 Years Ago Today; A Firing Exercise goes terribly wrong in Turret 2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USS_Iowa_turret_explosion

Debris and smoke fly through the air as USS Iowa's Turret Two's center gun explodes
USS Iowa turret explosion
On 19 April 1989, the Number Two 16-inch gun turret of the United States Navy battleship USS Iowa (BB-61) exploded. The explosion in the center gun room killed 47 of the turret's crewmen and severely damaged the gun turret itself. Two major investigations were undertaken into the cause of the explosion, one by the U.S. Navy and then one by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) and Sandia National Laboratories. The investigations produced conflicting conclusions.
The first investigation into the explosion, conducted by the U.S. Navy, concluded that one of the gun turret crew members, Clayton Hartwig, who died in the explosion, had deliberately caused it. During the investigation, numerous leaks to the media, later attributed to U.S. Navy officers and investigators, implied that Hartwig and another sailor, Kendall Truitt, had engaged in a homosexual relationship and that Hartwig had caused the explosion after their relationship had soured. In its report, however, the U.S. Navy concluded that the evidence did not show that Hartwig was homosexual but that he was suicidal and had caused the explosion with either an electronic or chemical detonator.
The victims' families, the media, and members of the U.S. Congress were sharply critical of the U.S. Navy's findings. The U.S. Senate and U.S. House Armed Services Committees both held hearings to inquire into the Navy's investigation and later released reports disputing the U.S. Navy's conclusions. The Senate committee asked the GAO to review the U.S. Navy's investigation. To assist the GAO, Sandia National Laboratories provided a team of scientists to review the Navy's technical investigation.
During its review, Sandia determined that a significant overram of the powder bags into the gun had occurred as it was being loaded and that the overram could have caused the explosion. A subsequent test by the Navy of the overram scenario confirmed that an overram could have caused an explosion in the gun breech. Sandia's technicians also found that the physical evidence did not support the U.S. Navy's theory that an electronic or chemical detonator had been used to initiate the explosion.
In response to the new findings, the U.S. Navy, with Sandia's assistance, reopened the investigation. In August 1991, Sandia and the GAO completed their reports, concluding that the explosion was likely caused by an accidental overram of powder bags into the breech of the 16-inch gun. The U.S. Navy, however, disagreed with Sandia's opinion and concluded that the cause of the explosion could not be determined. The U.S. Navy expressed regret (but did not offer apology) to Hartwig's family and closed its investigation.
<snip>
Preparation for fleet exercise
On 10 April the battleship was visited by commander of the US 2nd Fleet, Vice Admiral Jerome L. Johnson, and on 13 April Iowa sailed from Norfolk to participate in a fleet exercise in the Caribbean Sea near Puerto Rico. The exercise, titled "FLEETEX 3-89", began on or around 17 April under Johnson's command. Iowa served as Johnson's flagship during the exercise.
Throughout the night of 18 April, Turret Two's crew conducted a major overhaul of their turret in preparation for a firing exercise scheduled to take place the next day. The center gun's compressed air system, which cleansed the bore of sparks and debris each time the gun was fired, was not operating properly.
Also on 18 April, Iowa's fire-control officer, Lieutenant Leo Walsh, conducted a briefing to discuss the next day's main battery exercise. Moosally, Morse, Kissinger, and Costigan did not attend the briefing. During the briefing, Skelley announced that Turret Two would participate in an experiment of his design in which D-846 powder would be used to fire 2700 lb (1224.7 kg) shells.
The powder lots of D-846 were among the oldest on board Iowa, dating back to 1943–1945, and were designed to fire 1900 lb (861.8 kg) shells. In fact, printed on each D-846 powder canister were the words, "WARNING: Do Not Use with 2,700-pound projectiles." D-846 powder burned faster than normal powder, which meant that it exerted greater pressure on the shell when fired. Skelley explained that the experiment's purpose was to improve the accuracy of the guns. Skelley's plan was for Turret Two to fire ten 2,700-pound practice (no explosives) projectiles, two from the left gun and four rounds each from the center and right guns. Each shot was to use five bags of D-846, instead of the six bags normally used, and to fire at the empty ocean 17 nautical miles (20 mi; 30 km) away.
Ziegler was especially concerned about his center gun crew. The rammerman, Robert W. Backherms, was inexperienced, as were the powder car operator, Gary J. Fisk, the primerman, Reginald L. Johnson Jr., and the gun captain, Richard Errick Lawrence. To help supervise Lawrence, Ziegler assigned Gunner's Mate Second Class Clayton Hartwig, the former center gun captain, who had been excused from gun turret duty because of a pending reassignment to a new duty station in London, to the center gun's crew for the firing exercise. Because of the late hour, Ziegler did not inform Hartwig of his assignment until the morning of 19 April, shortly before the firing exercise was scheduled to begin.
The rammerman's position was of special concern, as ramming was considered the most dangerous part of loading the gun. The ram was used to first thrust the projectile and then the powder bags into the gun's breech. The ram speed used for the projectile was much faster (14 feet (4.3 m) per second) than that used for the lighter powder bags (1.5 feet (0.46 m) per second), but there was no safety device on the ram piston to prevent the rammerman from accidentally pushing the powder bags at the faster speed. Overramming the powder bags into the gun could subject the highly flammable powder to excessive friction and compression, with a resulting increased danger of premature combustion. Also, if the bags were pushed too far into the gun, a gap between the last bag and the primer might prevent the powder from igniting when the gun was fired, causing a misfire. None of Iowa's rammermen had any training or experience in ramming nonstandard five-bag loads into the guns. Complicating the task, as the rammerman was shoving the powder bags, he was also supposed to simultaneously operate a lever to shut the powder hoist door and lower the powder hoist car. Iowa crewmen later stated that Turret Two's center gun rammer would sometimes "take off" uncontrollably on its own at high speed. Furthermore, Backherms had never operated the ram before during a live fire shoot.
Explosion
At 08:31 on 19 April, the main turret crewmembers were ordered to their stations in Turrets One, Two, and Three. Thirty minutes later the turrets reported that they were manned, swiveled to starboard in firing position, and ready to begin the drill. Vice Admiral Johnson and his staff entered the bridge to watch the firing exercise. Iowa was 260 nautical miles (300 mi; 480 km) northeast of Puerto Rico, steaming at 15 knots (17 mph; 28 km/h).
Turret One fired first, beginning at 09:33. Turret One's left gun misfired and its crew was unable to get the gun to discharge. Moosally ordered Turret Two to load and fire a three-gun salvo. According to standard procedure, the misfire in Turret One should have been resolved first before proceeding further with the exercise.
Forty-four seconds after Moosally's order, Lieutenant Buch reported that Turret Two's right gun was loaded and ready to fire. Seventeen seconds later, he reported that the left gun was ready. A few seconds later, Errick Lawrence, in Turret Two's center gun room, reported to Ziegler over the turret's phone circuit that, "We have a problem here. We are not ready yet. We have a problem here."[30] Ziegler responded by announcing over the turret's phone circuit, "Left gun loaded, good job. Center gun is having a little trouble. We'll straighten that out." Mortensen, monitoring Turret Two's phone circuit from his position in Turret One, heard Buch confirm that the left and right guns were loaded. Lawrence then called out, "I'm not ready yet! I'm not ready yet!" Next, Ernie Hanyecz, Turret Two's leading petty officer suddenly called out, "Mort! Mort! Mort!" Ziegler shouted, "Oh, my God! The powder is smoldering!"[34] At this time, Ziegler may have opened the door from the turret officer's booth in the rear of the turret into the center gun room and yelled at the crew to get the breech closed. About this same time, Hanyecz yelled over the phone circuit, "Oh, my God! There's a flash!"

Iowa's Number Two turret is cooled with sea water shortly after exploding.
At 09:53, about 81 seconds after Moosally's order to load and 20 seconds after the left gun had reported loaded and ready, Turret Two's center gun exploded. A fireball between 2,500 and 3,000 °F (1,400 and 1,600 °C) and traveling at 2,000 feet per second (610 m/s) with a pressure of 4,000 pounds-force per square inch (28 MPa) blew out from the center gun's open breech. The explosion caved in the door between the center gun room and the turret officer's booth and buckled the bulkheads separating the center gun room from the left and right gun rooms. The fireball spread through all three gun rooms and through much of the lower levels of the turret. The resulting fire released toxic gases, including cyanide gas from burning polyurethane foam, which filled the turret. Shortly after the initial explosion, the heat and fire ignited 2,000 pounds (910 kg) of powder bags in the powder-handling area of the turret. Nine minutes later, another explosion, most likely caused by a buildup of carbon monoxide gas, occurred. All 47 crewmen inside the turret were killed. The turret contained most of the force of the explosion. Twelve crewmen working in or near the turret's powder magazine and annular spaces, located adjacent to the bottom of the turret, were able to escape without serious injury. These men were protected by blast doors which separate the magazine spaces from the rest of the turret.
Immediate aftermath
Firefighting crews quickly responded and sprayed the roof of the turret and left and right gun barrels, which were still loaded, with water. Meyer and Kissinger, wearing gas masks, descended below decks and inspected the powder flats in the turret, noting that the metal walls of the turret flats surrounding several tons of unexploded powder bags in the turret were now "glowing a bright cherry red". Meyer and Kissinger were accompanied by Gunner's Mate Third Class Noah Melendez in their inspection of the turret. On Kissinger's recommendation, Moosally ordered Turret Two's magazines, annular spaces, and powder flats flooded with seawater, preventing the remaining powder from exploding. The turret fire was extinguished in about 90 minutes. Brian Scanio was the first fireman to enter the burning turret, followed soon after by Robert O. Shepherd, Ronald G. Robb, and Thad W. Harms. The firemen deployed hoses inside the turret.
After the fire was extinguished, Mortensen entered the turret to help identify the bodies of the dead crewmen. Mortensen found Hartwig's body, which he identified by a distinctive tattoo on the upper left arm, at the bottom of the 20-foot (6.1 m) deep center gun pit instead of in the gun room. His body was missing his lower forearms, legs below the knees, and was partially, but not badly, charred. The gas ejection air valve for the center gun was located at the bottom of the pit, leading Mortensen to believe that Hartwig had been sent into the pit to turn it on before the explosion occurred. Mortensen also found that the center gun's powder hoist had not been lowered, which was unusual since the hoist door was closed and locked.

Navy pallbearers, attended by an honor guard, carry the remains of one of the victims from the turret explosion after its arrival at Dover Air Force Base on 20 April 1989.
After most of the water was pumped out, the bodies in the turret were removed without noting or photographing their locations. The next day, the bodies were flown from the ship by helicopter to Roosevelt Roads Naval Station, Puerto Rico. From there, they were flown on a United States Air Force C-5 Galaxy transport aircraft to the Charles C. Carson Center for Mortuary Affairs at Dover Air Force Base, Delaware. Meyer made a rudimentary sketch of the locations of the bodies in the turret which would later contradict some of the findings in the U.S. Navy's initial investigation. With assistance from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the U.S. Navy was able to complete identification of all 47 sets of remains on 16 May 1989. Contradicting FBI records, the U.S. Navy would insist that all the remains had been identified by 24 April 1989, when all of the bodies were released to the families. The FBI cut the fingers off the unidentified corpses to identify them later. Body parts which had not been matched to torsos were discarded. Many of the remains were released to family members for burial before they were positively identified. Most of the bodies recovered from the center gun and turret officer's booth were badly burned and in pieces, making identification difficult. The bodies discovered lower in the turret were mostly intact; those crewmen had apparently died from suffocation, poisonous gases, or from impact trauma after being thrown around by the explosion. An explosive ordnance disposal technician, Operations Specialist First Class James Bennett Drake, from the nearby USS Coral Sea was sent to Iowa to assist in unloading the powder in Turret Two's left and right guns. After observing the scene in the center gun room and asking some questions, Drake told Iowa crewmen that, "It's my opinion that the explosion started in the center gun room caused by compressing the powder bags against the sixteen-inch shell too far and too fast with the rammer arm". Drake also helped Mortensen unload the powder from Turret One's left gun. When Turret One's left gun's breech was opened, it was discovered that the bottom powder bag was turned sideways. The projectile in Turret One's left gun was left in place and was eventually fired four months later.
Morse directed a cleanup crew, supervised by Lieutenant Commander Bob Holman, to make Turret Two "look as normal as possible". Over the next day, the crew swept, cleaned, and painted the inside of the turret. Loose or damaged equipment was tossed into the ocean. No attempt was made to record the locations or conditions of damaged equipment in the turret. "No one was preserving the evidence," said Brian R. Scanio, a fireman present at the scene.[46] A team of Naval Investigative Service (NIS) investigators (the predecessor of the Naval Criminal Investigative Service or NCIS) stationed nearby on the aircraft carrier Coral Sea was told that their services in investigating Iowa's mishap were not needed. At the same time, Moosally called a meeting with all of his officers, except Meyer, who was working in Turret One, in the ship's wardroom. At the meeting, Iowa's legal officer, Lieutenant Commander Richard Bagley, instructed the ship's officers on how to limit their testimony during the forthcoming investigation into the explosion. Terry McGinn, who was present at the meeting, stated later that Bagley "told everybody what to say. It was a party line pure and simple".
On 23 April Iowa returned to Norfolk, where a memorial service was held on 24 April. Several thousand people, including family members of many of the victims, attended the ceremony at which President George H. W. Bush spoke. During his speech, Bush stated, "I promise you today, we will find out 'why,' the circumstances of this tragedy." In a press conference after the ceremony, Moosally said that the two legalmen killed in the turret were assigned there as "observers". He also claimed that everyone in the turret was qualified for the position that they were filling.
Shortly after the memorial service at Norfolk on 24 April, Kendall Truitt told Hartwig's family that Hartwig had taken out a $50,000 double indemnity life insurance policy on himself and named Truitt as the sole beneficiary. Truitt was a friend of Hartwig's and had been working in Turret Two's powder magazine at the time of the explosion, but had escaped without serious injury. Truitt promised to give the life insurance money to Hartwig's parents. Unsure if she could trust Truitt, Kathy Kubicina, Hartwig's sister, mailed letters on 4 May to Moosally, Morse, Costigan, Iowa's Chaplain Lieutenant Commander James Danner, and to Ohio Senators Howard Metzenbaum and John Glenn in which she described the life insurance policy. She asked that someone talk to Truitt to convince him to give the money to Hartwig's parents.
<snip>
Investigation conclusion
On 15 July 1989 Milligan submitted his completed report on the explosion to his chain of command. The 60-page report found that the explosion was a deliberate act "most probably" committed by Hartwig using an electronic timer. The report concluded that the powder bags had been overrammed into the center gun by 21 inches (53 cm), but had been done so under Hartwig's direction in order to trigger the explosive timer that he had placed between two of the powder bags.
Donnell, on 28 July, endorsed Milligan's report, saying that the determination that Hartwig had sabotaged the gun "leaves the reader incredulous, yet the opinion is supported by facts and analysis from which it flows logically and inevitably". Donnell's superior, Atlantic Fleet Commander Admiral Powell F. Carter, Jr., then endorsed the report, adding that the report showed that there were "substantial and serious failures by Moosally and Morse", and forwarded the report to the CNO, Carlisle Trost. Although Miceli had just announced that test results at Dahlgren showed that an electronic timer had not caused the explosion, Trost endorsed the report on 31 August, stating that Hartwig was "the individual who had motive, knowledge, and physical position within the turret gun room to place a device in the powder train". Trost's endorsement cited Smith's statement to the NIS as further evidence that Hartwig was the culprit. Milligan's report was not changed to reflect Miceli's new theory that a chemical igniter, not an electrical timer, had been used to initiate the explosion.
On 7 September, Milligan and Edney formally briefed media representatives at the Pentagon on the results of Milligan's investigation. Edney denied that the Navy had leaked any details about the investigation to the press. Milligan stated that the Navy believed Hartwig had caused the explosion, citing, among other evidence, the FBI's equivocal death analysis on Hartwig. Milligan displayed two books, Getting Even and Improvised Munitions Handbook, which he said belonged to Hartwig and provided "explicit" instructions on how to construct detonators and bombs. Milligan and Edney said that there was no proof that Hartwig was homosexual. Edney then stated that the investigation had proved that the Iowa-class battleships were safe to operate and that the powder in use on the ships "is stable and ready to use".
Most of the victims' family members criticized the Navy's conclusions. Many of the families told media representatives of private misgivings that the victims had expressed to them about problems with training and the dangerous gunfire experiments occurring on Iowa before the explosion. Hartwig's family disputed the allegations that he was depressed and suicidal.
Several journalists immediately began questioning the results of Milligan's investigation. John Hall, a reporter for the Richmond Times-Dispatch, wrote a series of four articles beginning on 17 September that revealed that Iowa was engaged in illegal powder experiments when the gun blew up; that conflicts of interest were evident in the investigators assigned to the inquiry; that many of the ship's crew were improperly or inadequately trained; and that evidence did not support the Navy's theory that Hartwig caused the explosion. The Associated Press picked up Hall's story and it was run in other newspapers throughout the United States. Robert Becker and A. J. Plunkett from the Daily Press wrote a lengthy story which criticized Milligan's report in detail. ABC reporter Robert Zelnick wrote an op-ed piece, which ran in The New York Times on 11 September, heavily criticizing the Navy for, in Zelnick's words, "scapegoating a dead seaman." Television newsmagazines 20/20 and 60 Minutes both ran stories questioning the Navy's conclusions. The Washington Post, in contrast, ran a story by George Wilson that generally supported the Navy's findings.
On 3 October, Donnell disciplined Iowa's officers in response to findings in Milligan's report. Moosally and Bob Finney, Iowa's operations officer, were given nonpunitive "letters of admonition" which were not placed in their permanent personnel records. Kissinger and Skelley received punitive letters of admonition which were placed in their records, as well as fines of $2,000 and $1,000 respectively. Donnell suspended both fines. Shortly thereafter, the Navy issued a statement explaining that the safety violations and training deficiencies found aboard Iowa during the investigation were unrelated to the explosion. Two weeks later, a panel of thirteen admirals recommended that Moosally be given another major command, stating that Moosally was "superbly fit" for such responsibility. Milligan was one of the admirals on the panel who supported the recommendation. After 60 Minutes producer Charles Thompson asked Brent Baker and Chief of Naval Personnel Jeremy Michael Boorda about the recommendation, Moosally's name was withdrawn.
</snip>

Debris and smoke fly through the air as USS Iowa's Turret Two's center gun explodes
USS Iowa turret explosion
On 19 April 1989, the Number Two 16-inch gun turret of the United States Navy battleship USS Iowa (BB-61) exploded. The explosion in the center gun room killed 47 of the turret's crewmen and severely damaged the gun turret itself. Two major investigations were undertaken into the cause of the explosion, one by the U.S. Navy and then one by the Government Accountability Office (GAO) and Sandia National Laboratories. The investigations produced conflicting conclusions.
The first investigation into the explosion, conducted by the U.S. Navy, concluded that one of the gun turret crew members, Clayton Hartwig, who died in the explosion, had deliberately caused it. During the investigation, numerous leaks to the media, later attributed to U.S. Navy officers and investigators, implied that Hartwig and another sailor, Kendall Truitt, had engaged in a homosexual relationship and that Hartwig had caused the explosion after their relationship had soured. In its report, however, the U.S. Navy concluded that the evidence did not show that Hartwig was homosexual but that he was suicidal and had caused the explosion with either an electronic or chemical detonator.
The victims' families, the media, and members of the U.S. Congress were sharply critical of the U.S. Navy's findings. The U.S. Senate and U.S. House Armed Services Committees both held hearings to inquire into the Navy's investigation and later released reports disputing the U.S. Navy's conclusions. The Senate committee asked the GAO to review the U.S. Navy's investigation. To assist the GAO, Sandia National Laboratories provided a team of scientists to review the Navy's technical investigation.
During its review, Sandia determined that a significant overram of the powder bags into the gun had occurred as it was being loaded and that the overram could have caused the explosion. A subsequent test by the Navy of the overram scenario confirmed that an overram could have caused an explosion in the gun breech. Sandia's technicians also found that the physical evidence did not support the U.S. Navy's theory that an electronic or chemical detonator had been used to initiate the explosion.
In response to the new findings, the U.S. Navy, with Sandia's assistance, reopened the investigation. In August 1991, Sandia and the GAO completed their reports, concluding that the explosion was likely caused by an accidental overram of powder bags into the breech of the 16-inch gun. The U.S. Navy, however, disagreed with Sandia's opinion and concluded that the cause of the explosion could not be determined. The U.S. Navy expressed regret (but did not offer apology) to Hartwig's family and closed its investigation.
<snip>
Preparation for fleet exercise
On 10 April the battleship was visited by commander of the US 2nd Fleet, Vice Admiral Jerome L. Johnson, and on 13 April Iowa sailed from Norfolk to participate in a fleet exercise in the Caribbean Sea near Puerto Rico. The exercise, titled "FLEETEX 3-89", began on or around 17 April under Johnson's command. Iowa served as Johnson's flagship during the exercise.
Throughout the night of 18 April, Turret Two's crew conducted a major overhaul of their turret in preparation for a firing exercise scheduled to take place the next day. The center gun's compressed air system, which cleansed the bore of sparks and debris each time the gun was fired, was not operating properly.
Also on 18 April, Iowa's fire-control officer, Lieutenant Leo Walsh, conducted a briefing to discuss the next day's main battery exercise. Moosally, Morse, Kissinger, and Costigan did not attend the briefing. During the briefing, Skelley announced that Turret Two would participate in an experiment of his design in which D-846 powder would be used to fire 2700 lb (1224.7 kg) shells.
The powder lots of D-846 were among the oldest on board Iowa, dating back to 1943–1945, and were designed to fire 1900 lb (861.8 kg) shells. In fact, printed on each D-846 powder canister were the words, "WARNING: Do Not Use with 2,700-pound projectiles." D-846 powder burned faster than normal powder, which meant that it exerted greater pressure on the shell when fired. Skelley explained that the experiment's purpose was to improve the accuracy of the guns. Skelley's plan was for Turret Two to fire ten 2,700-pound practice (no explosives) projectiles, two from the left gun and four rounds each from the center and right guns. Each shot was to use five bags of D-846, instead of the six bags normally used, and to fire at the empty ocean 17 nautical miles (20 mi; 30 km) away.
Ziegler was especially concerned about his center gun crew. The rammerman, Robert W. Backherms, was inexperienced, as were the powder car operator, Gary J. Fisk, the primerman, Reginald L. Johnson Jr., and the gun captain, Richard Errick Lawrence. To help supervise Lawrence, Ziegler assigned Gunner's Mate Second Class Clayton Hartwig, the former center gun captain, who had been excused from gun turret duty because of a pending reassignment to a new duty station in London, to the center gun's crew for the firing exercise. Because of the late hour, Ziegler did not inform Hartwig of his assignment until the morning of 19 April, shortly before the firing exercise was scheduled to begin.
The rammerman's position was of special concern, as ramming was considered the most dangerous part of loading the gun. The ram was used to first thrust the projectile and then the powder bags into the gun's breech. The ram speed used for the projectile was much faster (14 feet (4.3 m) per second) than that used for the lighter powder bags (1.5 feet (0.46 m) per second), but there was no safety device on the ram piston to prevent the rammerman from accidentally pushing the powder bags at the faster speed. Overramming the powder bags into the gun could subject the highly flammable powder to excessive friction and compression, with a resulting increased danger of premature combustion. Also, if the bags were pushed too far into the gun, a gap between the last bag and the primer might prevent the powder from igniting when the gun was fired, causing a misfire. None of Iowa's rammermen had any training or experience in ramming nonstandard five-bag loads into the guns. Complicating the task, as the rammerman was shoving the powder bags, he was also supposed to simultaneously operate a lever to shut the powder hoist door and lower the powder hoist car. Iowa crewmen later stated that Turret Two's center gun rammer would sometimes "take off" uncontrollably on its own at high speed. Furthermore, Backherms had never operated the ram before during a live fire shoot.
Explosion
At 08:31 on 19 April, the main turret crewmembers were ordered to their stations in Turrets One, Two, and Three. Thirty minutes later the turrets reported that they were manned, swiveled to starboard in firing position, and ready to begin the drill. Vice Admiral Johnson and his staff entered the bridge to watch the firing exercise. Iowa was 260 nautical miles (300 mi; 480 km) northeast of Puerto Rico, steaming at 15 knots (17 mph; 28 km/h).
Turret One fired first, beginning at 09:33. Turret One's left gun misfired and its crew was unable to get the gun to discharge. Moosally ordered Turret Two to load and fire a three-gun salvo. According to standard procedure, the misfire in Turret One should have been resolved first before proceeding further with the exercise.
Forty-four seconds after Moosally's order, Lieutenant Buch reported that Turret Two's right gun was loaded and ready to fire. Seventeen seconds later, he reported that the left gun was ready. A few seconds later, Errick Lawrence, in Turret Two's center gun room, reported to Ziegler over the turret's phone circuit that, "We have a problem here. We are not ready yet. We have a problem here."[30] Ziegler responded by announcing over the turret's phone circuit, "Left gun loaded, good job. Center gun is having a little trouble. We'll straighten that out." Mortensen, monitoring Turret Two's phone circuit from his position in Turret One, heard Buch confirm that the left and right guns were loaded. Lawrence then called out, "I'm not ready yet! I'm not ready yet!" Next, Ernie Hanyecz, Turret Two's leading petty officer suddenly called out, "Mort! Mort! Mort!" Ziegler shouted, "Oh, my God! The powder is smoldering!"[34] At this time, Ziegler may have opened the door from the turret officer's booth in the rear of the turret into the center gun room and yelled at the crew to get the breech closed. About this same time, Hanyecz yelled over the phone circuit, "Oh, my God! There's a flash!"

Iowa's Number Two turret is cooled with sea water shortly after exploding.
At 09:53, about 81 seconds after Moosally's order to load and 20 seconds after the left gun had reported loaded and ready, Turret Two's center gun exploded. A fireball between 2,500 and 3,000 °F (1,400 and 1,600 °C) and traveling at 2,000 feet per second (610 m/s) with a pressure of 4,000 pounds-force per square inch (28 MPa) blew out from the center gun's open breech. The explosion caved in the door between the center gun room and the turret officer's booth and buckled the bulkheads separating the center gun room from the left and right gun rooms. The fireball spread through all three gun rooms and through much of the lower levels of the turret. The resulting fire released toxic gases, including cyanide gas from burning polyurethane foam, which filled the turret. Shortly after the initial explosion, the heat and fire ignited 2,000 pounds (910 kg) of powder bags in the powder-handling area of the turret. Nine minutes later, another explosion, most likely caused by a buildup of carbon monoxide gas, occurred. All 47 crewmen inside the turret were killed. The turret contained most of the force of the explosion. Twelve crewmen working in or near the turret's powder magazine and annular spaces, located adjacent to the bottom of the turret, were able to escape without serious injury. These men were protected by blast doors which separate the magazine spaces from the rest of the turret.
Immediate aftermath
Firefighting crews quickly responded and sprayed the roof of the turret and left and right gun barrels, which were still loaded, with water. Meyer and Kissinger, wearing gas masks, descended below decks and inspected the powder flats in the turret, noting that the metal walls of the turret flats surrounding several tons of unexploded powder bags in the turret were now "glowing a bright cherry red". Meyer and Kissinger were accompanied by Gunner's Mate Third Class Noah Melendez in their inspection of the turret. On Kissinger's recommendation, Moosally ordered Turret Two's magazines, annular spaces, and powder flats flooded with seawater, preventing the remaining powder from exploding. The turret fire was extinguished in about 90 minutes. Brian Scanio was the first fireman to enter the burning turret, followed soon after by Robert O. Shepherd, Ronald G. Robb, and Thad W. Harms. The firemen deployed hoses inside the turret.
After the fire was extinguished, Mortensen entered the turret to help identify the bodies of the dead crewmen. Mortensen found Hartwig's body, which he identified by a distinctive tattoo on the upper left arm, at the bottom of the 20-foot (6.1 m) deep center gun pit instead of in the gun room. His body was missing his lower forearms, legs below the knees, and was partially, but not badly, charred. The gas ejection air valve for the center gun was located at the bottom of the pit, leading Mortensen to believe that Hartwig had been sent into the pit to turn it on before the explosion occurred. Mortensen also found that the center gun's powder hoist had not been lowered, which was unusual since the hoist door was closed and locked.

Navy pallbearers, attended by an honor guard, carry the remains of one of the victims from the turret explosion after its arrival at Dover Air Force Base on 20 April 1989.
After most of the water was pumped out, the bodies in the turret were removed without noting or photographing their locations. The next day, the bodies were flown from the ship by helicopter to Roosevelt Roads Naval Station, Puerto Rico. From there, they were flown on a United States Air Force C-5 Galaxy transport aircraft to the Charles C. Carson Center for Mortuary Affairs at Dover Air Force Base, Delaware. Meyer made a rudimentary sketch of the locations of the bodies in the turret which would later contradict some of the findings in the U.S. Navy's initial investigation. With assistance from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the U.S. Navy was able to complete identification of all 47 sets of remains on 16 May 1989. Contradicting FBI records, the U.S. Navy would insist that all the remains had been identified by 24 April 1989, when all of the bodies were released to the families. The FBI cut the fingers off the unidentified corpses to identify them later. Body parts which had not been matched to torsos were discarded. Many of the remains were released to family members for burial before they were positively identified. Most of the bodies recovered from the center gun and turret officer's booth were badly burned and in pieces, making identification difficult. The bodies discovered lower in the turret were mostly intact; those crewmen had apparently died from suffocation, poisonous gases, or from impact trauma after being thrown around by the explosion. An explosive ordnance disposal technician, Operations Specialist First Class James Bennett Drake, from the nearby USS Coral Sea was sent to Iowa to assist in unloading the powder in Turret Two's left and right guns. After observing the scene in the center gun room and asking some questions, Drake told Iowa crewmen that, "It's my opinion that the explosion started in the center gun room caused by compressing the powder bags against the sixteen-inch shell too far and too fast with the rammer arm". Drake also helped Mortensen unload the powder from Turret One's left gun. When Turret One's left gun's breech was opened, it was discovered that the bottom powder bag was turned sideways. The projectile in Turret One's left gun was left in place and was eventually fired four months later.
Morse directed a cleanup crew, supervised by Lieutenant Commander Bob Holman, to make Turret Two "look as normal as possible". Over the next day, the crew swept, cleaned, and painted the inside of the turret. Loose or damaged equipment was tossed into the ocean. No attempt was made to record the locations or conditions of damaged equipment in the turret. "No one was preserving the evidence," said Brian R. Scanio, a fireman present at the scene.[46] A team of Naval Investigative Service (NIS) investigators (the predecessor of the Naval Criminal Investigative Service or NCIS) stationed nearby on the aircraft carrier Coral Sea was told that their services in investigating Iowa's mishap were not needed. At the same time, Moosally called a meeting with all of his officers, except Meyer, who was working in Turret One, in the ship's wardroom. At the meeting, Iowa's legal officer, Lieutenant Commander Richard Bagley, instructed the ship's officers on how to limit their testimony during the forthcoming investigation into the explosion. Terry McGinn, who was present at the meeting, stated later that Bagley "told everybody what to say. It was a party line pure and simple".
On 23 April Iowa returned to Norfolk, where a memorial service was held on 24 April. Several thousand people, including family members of many of the victims, attended the ceremony at which President George H. W. Bush spoke. During his speech, Bush stated, "I promise you today, we will find out 'why,' the circumstances of this tragedy." In a press conference after the ceremony, Moosally said that the two legalmen killed in the turret were assigned there as "observers". He also claimed that everyone in the turret was qualified for the position that they were filling.
Shortly after the memorial service at Norfolk on 24 April, Kendall Truitt told Hartwig's family that Hartwig had taken out a $50,000 double indemnity life insurance policy on himself and named Truitt as the sole beneficiary. Truitt was a friend of Hartwig's and had been working in Turret Two's powder magazine at the time of the explosion, but had escaped without serious injury. Truitt promised to give the life insurance money to Hartwig's parents. Unsure if she could trust Truitt, Kathy Kubicina, Hartwig's sister, mailed letters on 4 May to Moosally, Morse, Costigan, Iowa's Chaplain Lieutenant Commander James Danner, and to Ohio Senators Howard Metzenbaum and John Glenn in which she described the life insurance policy. She asked that someone talk to Truitt to convince him to give the money to Hartwig's parents.
<snip>
Investigation conclusion
On 15 July 1989 Milligan submitted his completed report on the explosion to his chain of command. The 60-page report found that the explosion was a deliberate act "most probably" committed by Hartwig using an electronic timer. The report concluded that the powder bags had been overrammed into the center gun by 21 inches (53 cm), but had been done so under Hartwig's direction in order to trigger the explosive timer that he had placed between two of the powder bags.
Donnell, on 28 July, endorsed Milligan's report, saying that the determination that Hartwig had sabotaged the gun "leaves the reader incredulous, yet the opinion is supported by facts and analysis from which it flows logically and inevitably". Donnell's superior, Atlantic Fleet Commander Admiral Powell F. Carter, Jr., then endorsed the report, adding that the report showed that there were "substantial and serious failures by Moosally and Morse", and forwarded the report to the CNO, Carlisle Trost. Although Miceli had just announced that test results at Dahlgren showed that an electronic timer had not caused the explosion, Trost endorsed the report on 31 August, stating that Hartwig was "the individual who had motive, knowledge, and physical position within the turret gun room to place a device in the powder train". Trost's endorsement cited Smith's statement to the NIS as further evidence that Hartwig was the culprit. Milligan's report was not changed to reflect Miceli's new theory that a chemical igniter, not an electrical timer, had been used to initiate the explosion.
On 7 September, Milligan and Edney formally briefed media representatives at the Pentagon on the results of Milligan's investigation. Edney denied that the Navy had leaked any details about the investigation to the press. Milligan stated that the Navy believed Hartwig had caused the explosion, citing, among other evidence, the FBI's equivocal death analysis on Hartwig. Milligan displayed two books, Getting Even and Improvised Munitions Handbook, which he said belonged to Hartwig and provided "explicit" instructions on how to construct detonators and bombs. Milligan and Edney said that there was no proof that Hartwig was homosexual. Edney then stated that the investigation had proved that the Iowa-class battleships were safe to operate and that the powder in use on the ships "is stable and ready to use".
Most of the victims' family members criticized the Navy's conclusions. Many of the families told media representatives of private misgivings that the victims had expressed to them about problems with training and the dangerous gunfire experiments occurring on Iowa before the explosion. Hartwig's family disputed the allegations that he was depressed and suicidal.
Several journalists immediately began questioning the results of Milligan's investigation. John Hall, a reporter for the Richmond Times-Dispatch, wrote a series of four articles beginning on 17 September that revealed that Iowa was engaged in illegal powder experiments when the gun blew up; that conflicts of interest were evident in the investigators assigned to the inquiry; that many of the ship's crew were improperly or inadequately trained; and that evidence did not support the Navy's theory that Hartwig caused the explosion. The Associated Press picked up Hall's story and it was run in other newspapers throughout the United States. Robert Becker and A. J. Plunkett from the Daily Press wrote a lengthy story which criticized Milligan's report in detail. ABC reporter Robert Zelnick wrote an op-ed piece, which ran in The New York Times on 11 September, heavily criticizing the Navy for, in Zelnick's words, "scapegoating a dead seaman." Television newsmagazines 20/20 and 60 Minutes both ran stories questioning the Navy's conclusions. The Washington Post, in contrast, ran a story by George Wilson that generally supported the Navy's findings.
On 3 October, Donnell disciplined Iowa's officers in response to findings in Milligan's report. Moosally and Bob Finney, Iowa's operations officer, were given nonpunitive "letters of admonition" which were not placed in their permanent personnel records. Kissinger and Skelley received punitive letters of admonition which were placed in their records, as well as fines of $2,000 and $1,000 respectively. Donnell suspended both fines. Shortly thereafter, the Navy issued a statement explaining that the safety violations and training deficiencies found aboard Iowa during the investigation were unrelated to the explosion. Two weeks later, a panel of thirteen admirals recommended that Moosally be given another major command, stating that Moosally was "superbly fit" for such responsibility. Milligan was one of the admirals on the panel who supported the recommendation. After 60 Minutes producer Charles Thompson asked Brent Baker and Chief of Naval Personnel Jeremy Michael Boorda about the recommendation, Moosally's name was withdrawn.
</snip>
April 18, 2019















 <- for all 16 crews
<- for all 16 crews
77 Years Ago Today; 30 Seconds Over Tokyo
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doolittle_Raid

The Doolittle Raid, also known as the Tokyo Raid, on Saturday, April 18, 1942, was an air raid by the United States on the Japanese capital Tokyo and other places on the island of Honshu during World War II, the first air operation to strike the Japanese Home Islands. It demonstrated that the Japanese mainland was vulnerable to American air attack, served as retaliation for the attack on Pearl Harbor, and provided an important boost to American morale. The raid was planned and led by Lieutenant Colonel James Doolittle of the United States Army Air Forces.
Sixteen B-25B Mitchell medium bombers were launched without fighter escort from the U.S. Navy's aircraft carrier USS Hornet (CV-8) deep in the Western Pacific Ocean, each with a crew of five men. The plan called for them to bomb military targets in Japan, and to continue westward to land in China—landing a medium bomber on Hornet was impossible. The bombing raid killed about 50 people, including civilians, and injured 400. Fifteen aircraft reached China, but all crashed, while the 16th landed at Vladivostok in the Soviet Union. Of the 80 crew members, 77 initially survived the mission. Eight airmen were captured by the Japanese Army in China; three of those were later executed. The B-25 that landed in the Soviet Union was confiscated, with its crew interned for more than a year before being allowed to "escape" via Soviet-occupied Iran. Fourteen complete crews of five, except for one crewman who was killed in action, returned either to the United States, or to American forces.
After the raid, the Japanese Army conducted a massive sweep through the eastern coastal provinces of China, in an operation now known as the Zhejiang-Jiangxi campaign, searching for the surviving American airmen and inflicting retribution on the Chinese who aided them, in an effort to prevent this part of China from being used again for an attack on Japan.
The raid caused negligible material damage to Japan, but it had major psychological effects. In the United States, it raised morale. In Japan, it raised doubt about the ability of military leaders to defend the home islands, but the bombing and strafing of civilians also steeled the resolve to gain retribution and was exploited for propaganda purposes. It also contributed to Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto's decision to attack Midway Island in the Central Pacific—an attack that turned into a decisive strategic defeat of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) by the U.S. Navy in the Battle of Midway. The consequences were most severely felt in China, where Japanese reprisals cost an estimated 250,000 lives.
Doolittle, who initially believed that the loss of all his aircraft would lead to his court-martial, received the Medal of Honor and was promoted two ranks to brigadier general.
<snip>
Mission

B-25Bs on the USS Hornet en route to Japan
On 1 April 1942, the 16 modified bombers, their five-man crews, and Army maintenance personnel, totaling 71 officers and 130 enlisted men, were loaded onto the USS Hornet at Naval Air Station Alameda. Each aircraft carried four specially constructed 500-pound (225-kg) bombs. Three of these were high-explosive munitions and one was a bundle of incendiaries. The incendiaries were long tubes, wrapped together to be carried in the bomb bay, but designed to separate and scatter over a wide area after release. Five bombs had Japanese "friendship" medals wired to them—medals awarded by the Japanese government to U.S. servicemen before the war.
The bombers' armament was reduced to increase range by decreasing weight. Each bomber launched with two .50-caliber (12.7-mm) machine guns in an upper turret and a .30-caliber (7.62-mm) machine gun in the nose. The aircraft were clustered closely and tied down on Hornet's flight deck in the order of launch.

Orders in hand, Navy Capt. Marc A. Mitscher, skipper of the USS Hornet, chats with Lt. Col. James Doolittle.
Hornet and Task Force 18 got underway from San Francisco Bay at 08:48 on 2 April with the 16 bombers in clear view. At noon the next day, parts to complete modifications that had not been finished at McClellan were lowered to the forward deck of the Hornet by Navy blimp L-8. A few days later, the carrier met with Task Force 16, commanded by Vice Admiral William F. Halsey, Jr.—the carrier USS Enterprise and her escort of cruisers and destroyers in the mid-Pacific Ocean north of Hawaii. Enterprise's fighters and scout planes provided protection for the entire task force in the event of a Japanese air attack, since Hornet's fighters were stowed below decks to allow the B-25s to use the flight deck.
The combined force was two carriers (Hornet and Enterprise), three heavy cruisers (Salt Lake City, Northampton, Vincennes), one light cruiser (Nashville), eight destroyers (Balch, Fanning, Benham, Ellet, Gwin, Meredith, Grayson, Monssen), and two fleet oilers (Cimarron and Sabine). The ships proceeded in radio silence. On the afternoon of 17 April, the slow oilers refueled the task force, then withdrew with the destroyers to the east while the carriers and cruisers dashed west at 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) toward their intended launch point in enemy-controlled waters east of Japan.
At 07:38 on the morning of 18 April, while the task force was still about 650 nautical miles (1,200 km; 750 mi) from Japan (around 35°N 154°E), it was sighted by the Japanese picket boat No. 23 Nittō Maru, a 70-ton patrol craft, which radioed an attack warning to Japan. The boat was sunk by gunfire from USS Nashville. The chief petty officer who captained the boat killed himself rather than be captured, but five of the 11 crew were picked up by Nashville.
Doolittle and Hornet skipper Captain Marc Mitscher decided to launch the B-25s immediately—10 hours early and 170 nautical miles (310 km; 200 mi) farther from Japan than planned. After respotting to allow for engine start and runups, Doolittle's aircraft had 467 feet (142 m) of takeoff distance. Although none of the B-25 pilots, including Doolittle, had ever taken off from a carrier before, all 16 aircraft launched safely between 08:20 and 09:19. The B-25s then flew toward Japan, most in groups of two to four aircraft, before flying singly at wave-top level to avoid detection.

Doolittle's B-25 at launching, 18 April 1942
The aircraft began arriving over Japan about noon Tokyo time, six hours after launch, climbed to 1,500 feet (460 m) and bombed 10 military and industrial targets in Tokyo, two in Yokohama, and one each in Yokosuka, Nagoya, Kobe, and Osaka. Although some B-25s encountered light antiaircraft fire and a few enemy fighters (made up of Ki-45s and prototype Ki-61s, the latter being mistaken for Bf 109s) over Japan, no bomber was shot down. Only the B-25 of 1st Lt. Richard O. Joyce received any battle damage, minor hits from antiaircraft fire. B-25 No. 4, piloted by 1st Lt. Everett W. Holstrom, jettisoned its bombs before reaching its target when it came under attack by fighters after its gun turret malfunctioned.
The Americans claimed to have shot down three Japanese fighters – one by the gunners of the Whirling Dervish, piloted by 1st Lt. Harold Watson, and two by the gunners of the Hari Kari-er, piloted by 1st Lt. Ross Greening. Many targets were strafed by the bombers' nose gunners. The subterfuge of the simulated gun barrels mounted in the tail cones was described afterwards by Doolittle as effective, in that no airplane was attacked from directly behind.
Fifteen of the 16 aircraft then proceeded southwest off the southeastern coast of Japan and across the East China Sea toward eastern China. One B-25, piloted by Captain Edward J. York, was extremely low on fuel, and headed instead for the Soviet Union rather than be forced to ditch in the middle of the East China Sea. Several fields in Zhejiang province were supposed to be ready to guide them in using homing beacons, then recover and refuel them for continuing on to Chongqing, the wartime Kuomintang capital. The primary base was at Zhuzhou, toward which all the aircraft navigated, but Halsey never sent the planned signal to alert them, apparently because of a possible threat to the task force.
The raiders faced several unforeseen challenges during their flight to China: night was approaching, the aircraft were running low on fuel, and the weather was rapidly deteriorating. None would have reached China if not for a tail wind as they came off the target, which increased their ground speed by 25 kn (46 km/h; 29 mph) for seven hours. The crews realized they would probably not be able to reach their intended bases in China, leaving them the option of either bailing out over eastern China or crash-landing along the Chinese coast.
All 15 aircraft reached the Chinese coast after 13 hours of flight and crash-landed or the crews bailed out. One crewman, 20-year-old Corporal Leland D. Faktor, flight engineer/gunner with 1st Lt. Robert M. Gray, was killed during his bailout attempt over China, the only man in that crew to be lost. Two crews (10 men) were missing. The 16th aircraft, commanded by Capt. Edward York (eighth off—AC #40-2242) flew to the Soviet Union and landed 40 miles (65 km) beyond Vladivostok at Vozdvizhenka, where their B-25 was confiscated and the crew interned.
Although York and his crew were treated well, diplomatic attempts to return them to the United States ultimately failed, as the Soviet Union was not at war with Japan and therefore obligated under international law to intern any combatants found on its soil. Eventually, they were relocated to Ashkhabad, 20 miles (32 km) from the Iranian border, and York managed to "bribe" a smuggler, who helped them cross the border into Iran, which at the time was under British-Soviet occupation. From there, the Americans were able to reach a nearby British consulate on 11 May 1943. The smuggling was actually staged by the NKVD, according to declassified Soviet archives, because the Soviet government was unable to repatriate them legally in the face of the neutrality pact with Japan and unwilling to openly flout its treaty obligations with Japan in light of the fact that Vladivostok and the rest of the Soviet Far East were essentially defenceless in the face of any potential Japanese retaliation. Nevertheless, by the time of the American aircrew's "escape" from Soviet internment, Japan's armed forces were clearly on the defensive and drawing down their strength in Manchuria in order to reinforce other fronts. Meanwhile, Soviet forces had gained the strategic initiative in Europe. Even if the Americans' "escape" managed to gain significant attention in Tokyo, it was by then thought extremely unlikely that Japan would respond with any sort of military retaliation.
Doolittle and his crew, after parachuting into China, received assistance from Chinese soldiers and civilians, as well as John Birch, an American missionary in China. As did the others who participated in the mission, Doolittle had to bail out, but he landed in a heap of dung (saving a previously injured ankle from breaking) in a paddy in China near Quzhou. The mission was the longest ever flown in combat by the B-25 Mitchell medium bomber, averaging about 2,250 nautical miles (4,170 km).
<snip>

The Doolittle Raid, also known as the Tokyo Raid, on Saturday, April 18, 1942, was an air raid by the United States on the Japanese capital Tokyo and other places on the island of Honshu during World War II, the first air operation to strike the Japanese Home Islands. It demonstrated that the Japanese mainland was vulnerable to American air attack, served as retaliation for the attack on Pearl Harbor, and provided an important boost to American morale. The raid was planned and led by Lieutenant Colonel James Doolittle of the United States Army Air Forces.
Sixteen B-25B Mitchell medium bombers were launched without fighter escort from the U.S. Navy's aircraft carrier USS Hornet (CV-8) deep in the Western Pacific Ocean, each with a crew of five men. The plan called for them to bomb military targets in Japan, and to continue westward to land in China—landing a medium bomber on Hornet was impossible. The bombing raid killed about 50 people, including civilians, and injured 400. Fifteen aircraft reached China, but all crashed, while the 16th landed at Vladivostok in the Soviet Union. Of the 80 crew members, 77 initially survived the mission. Eight airmen were captured by the Japanese Army in China; three of those were later executed. The B-25 that landed in the Soviet Union was confiscated, with its crew interned for more than a year before being allowed to "escape" via Soviet-occupied Iran. Fourteen complete crews of five, except for one crewman who was killed in action, returned either to the United States, or to American forces.
After the raid, the Japanese Army conducted a massive sweep through the eastern coastal provinces of China, in an operation now known as the Zhejiang-Jiangxi campaign, searching for the surviving American airmen and inflicting retribution on the Chinese who aided them, in an effort to prevent this part of China from being used again for an attack on Japan.
The raid caused negligible material damage to Japan, but it had major psychological effects. In the United States, it raised morale. In Japan, it raised doubt about the ability of military leaders to defend the home islands, but the bombing and strafing of civilians also steeled the resolve to gain retribution and was exploited for propaganda purposes. It also contributed to Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto's decision to attack Midway Island in the Central Pacific—an attack that turned into a decisive strategic defeat of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) by the U.S. Navy in the Battle of Midway. The consequences were most severely felt in China, where Japanese reprisals cost an estimated 250,000 lives.
Doolittle, who initially believed that the loss of all his aircraft would lead to his court-martial, received the Medal of Honor and was promoted two ranks to brigadier general.
<snip>
Mission

B-25Bs on the USS Hornet en route to Japan
On 1 April 1942, the 16 modified bombers, their five-man crews, and Army maintenance personnel, totaling 71 officers and 130 enlisted men, were loaded onto the USS Hornet at Naval Air Station Alameda. Each aircraft carried four specially constructed 500-pound (225-kg) bombs. Three of these were high-explosive munitions and one was a bundle of incendiaries. The incendiaries were long tubes, wrapped together to be carried in the bomb bay, but designed to separate and scatter over a wide area after release. Five bombs had Japanese "friendship" medals wired to them—medals awarded by the Japanese government to U.S. servicemen before the war.
The bombers' armament was reduced to increase range by decreasing weight. Each bomber launched with two .50-caliber (12.7-mm) machine guns in an upper turret and a .30-caliber (7.62-mm) machine gun in the nose. The aircraft were clustered closely and tied down on Hornet's flight deck in the order of launch.

Orders in hand, Navy Capt. Marc A. Mitscher, skipper of the USS Hornet, chats with Lt. Col. James Doolittle.
Hornet and Task Force 18 got underway from San Francisco Bay at 08:48 on 2 April with the 16 bombers in clear view. At noon the next day, parts to complete modifications that had not been finished at McClellan were lowered to the forward deck of the Hornet by Navy blimp L-8. A few days later, the carrier met with Task Force 16, commanded by Vice Admiral William F. Halsey, Jr.—the carrier USS Enterprise and her escort of cruisers and destroyers in the mid-Pacific Ocean north of Hawaii. Enterprise's fighters and scout planes provided protection for the entire task force in the event of a Japanese air attack, since Hornet's fighters were stowed below decks to allow the B-25s to use the flight deck.
The combined force was two carriers (Hornet and Enterprise), three heavy cruisers (Salt Lake City, Northampton, Vincennes), one light cruiser (Nashville), eight destroyers (Balch, Fanning, Benham, Ellet, Gwin, Meredith, Grayson, Monssen), and two fleet oilers (Cimarron and Sabine). The ships proceeded in radio silence. On the afternoon of 17 April, the slow oilers refueled the task force, then withdrew with the destroyers to the east while the carriers and cruisers dashed west at 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) toward their intended launch point in enemy-controlled waters east of Japan.
At 07:38 on the morning of 18 April, while the task force was still about 650 nautical miles (1,200 km; 750 mi) from Japan (around 35°N 154°E), it was sighted by the Japanese picket boat No. 23 Nittō Maru, a 70-ton patrol craft, which radioed an attack warning to Japan. The boat was sunk by gunfire from USS Nashville. The chief petty officer who captained the boat killed himself rather than be captured, but five of the 11 crew were picked up by Nashville.
Doolittle and Hornet skipper Captain Marc Mitscher decided to launch the B-25s immediately—10 hours early and 170 nautical miles (310 km; 200 mi) farther from Japan than planned. After respotting to allow for engine start and runups, Doolittle's aircraft had 467 feet (142 m) of takeoff distance. Although none of the B-25 pilots, including Doolittle, had ever taken off from a carrier before, all 16 aircraft launched safely between 08:20 and 09:19. The B-25s then flew toward Japan, most in groups of two to four aircraft, before flying singly at wave-top level to avoid detection.

Doolittle's B-25 at launching, 18 April 1942
The aircraft began arriving over Japan about noon Tokyo time, six hours after launch, climbed to 1,500 feet (460 m) and bombed 10 military and industrial targets in Tokyo, two in Yokohama, and one each in Yokosuka, Nagoya, Kobe, and Osaka. Although some B-25s encountered light antiaircraft fire and a few enemy fighters (made up of Ki-45s and prototype Ki-61s, the latter being mistaken for Bf 109s) over Japan, no bomber was shot down. Only the B-25 of 1st Lt. Richard O. Joyce received any battle damage, minor hits from antiaircraft fire. B-25 No. 4, piloted by 1st Lt. Everett W. Holstrom, jettisoned its bombs before reaching its target when it came under attack by fighters after its gun turret malfunctioned.
The Americans claimed to have shot down three Japanese fighters – one by the gunners of the Whirling Dervish, piloted by 1st Lt. Harold Watson, and two by the gunners of the Hari Kari-er, piloted by 1st Lt. Ross Greening. Many targets were strafed by the bombers' nose gunners. The subterfuge of the simulated gun barrels mounted in the tail cones was described afterwards by Doolittle as effective, in that no airplane was attacked from directly behind.
Fifteen of the 16 aircraft then proceeded southwest off the southeastern coast of Japan and across the East China Sea toward eastern China. One B-25, piloted by Captain Edward J. York, was extremely low on fuel, and headed instead for the Soviet Union rather than be forced to ditch in the middle of the East China Sea. Several fields in Zhejiang province were supposed to be ready to guide them in using homing beacons, then recover and refuel them for continuing on to Chongqing, the wartime Kuomintang capital. The primary base was at Zhuzhou, toward which all the aircraft navigated, but Halsey never sent the planned signal to alert them, apparently because of a possible threat to the task force.
The raiders faced several unforeseen challenges during their flight to China: night was approaching, the aircraft were running low on fuel, and the weather was rapidly deteriorating. None would have reached China if not for a tail wind as they came off the target, which increased their ground speed by 25 kn (46 km/h; 29 mph) for seven hours. The crews realized they would probably not be able to reach their intended bases in China, leaving them the option of either bailing out over eastern China or crash-landing along the Chinese coast.
All 15 aircraft reached the Chinese coast after 13 hours of flight and crash-landed or the crews bailed out. One crewman, 20-year-old Corporal Leland D. Faktor, flight engineer/gunner with 1st Lt. Robert M. Gray, was killed during his bailout attempt over China, the only man in that crew to be lost. Two crews (10 men) were missing. The 16th aircraft, commanded by Capt. Edward York (eighth off—AC #40-2242) flew to the Soviet Union and landed 40 miles (65 km) beyond Vladivostok at Vozdvizhenka, where their B-25 was confiscated and the crew interned.
Although York and his crew were treated well, diplomatic attempts to return them to the United States ultimately failed, as the Soviet Union was not at war with Japan and therefore obligated under international law to intern any combatants found on its soil. Eventually, they were relocated to Ashkhabad, 20 miles (32 km) from the Iranian border, and York managed to "bribe" a smuggler, who helped them cross the border into Iran, which at the time was under British-Soviet occupation. From there, the Americans were able to reach a nearby British consulate on 11 May 1943. The smuggling was actually staged by the NKVD, according to declassified Soviet archives, because the Soviet government was unable to repatriate them legally in the face of the neutrality pact with Japan and unwilling to openly flout its treaty obligations with Japan in light of the fact that Vladivostok and the rest of the Soviet Far East were essentially defenceless in the face of any potential Japanese retaliation. Nevertheless, by the time of the American aircrew's "escape" from Soviet internment, Japan's armed forces were clearly on the defensive and drawing down their strength in Manchuria in order to reinforce other fronts. Meanwhile, Soviet forces had gained the strategic initiative in Europe. Even if the Americans' "escape" managed to gain significant attention in Tokyo, it was by then thought extremely unlikely that Japan would respond with any sort of military retaliation.
Doolittle and his crew, after parachuting into China, received assistance from Chinese soldiers and civilians, as well as John Birch, an American missionary in China. As did the others who participated in the mission, Doolittle had to bail out, but he landed in a heap of dung (saving a previously injured ankle from breaking) in a paddy in China near Quzhou. The mission was the longest ever flown in combat by the B-25 Mitchell medium bomber, averaging about 2,250 nautical miles (4,170 km).
<snip>
April 17, 2019
I didn't realize that the West, TX explosion took place a day after the 66th anniversary of the Texas City Disaster.
6 Years Ago Today; Explosion in West, TX
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Fertilizer_Company_explosion
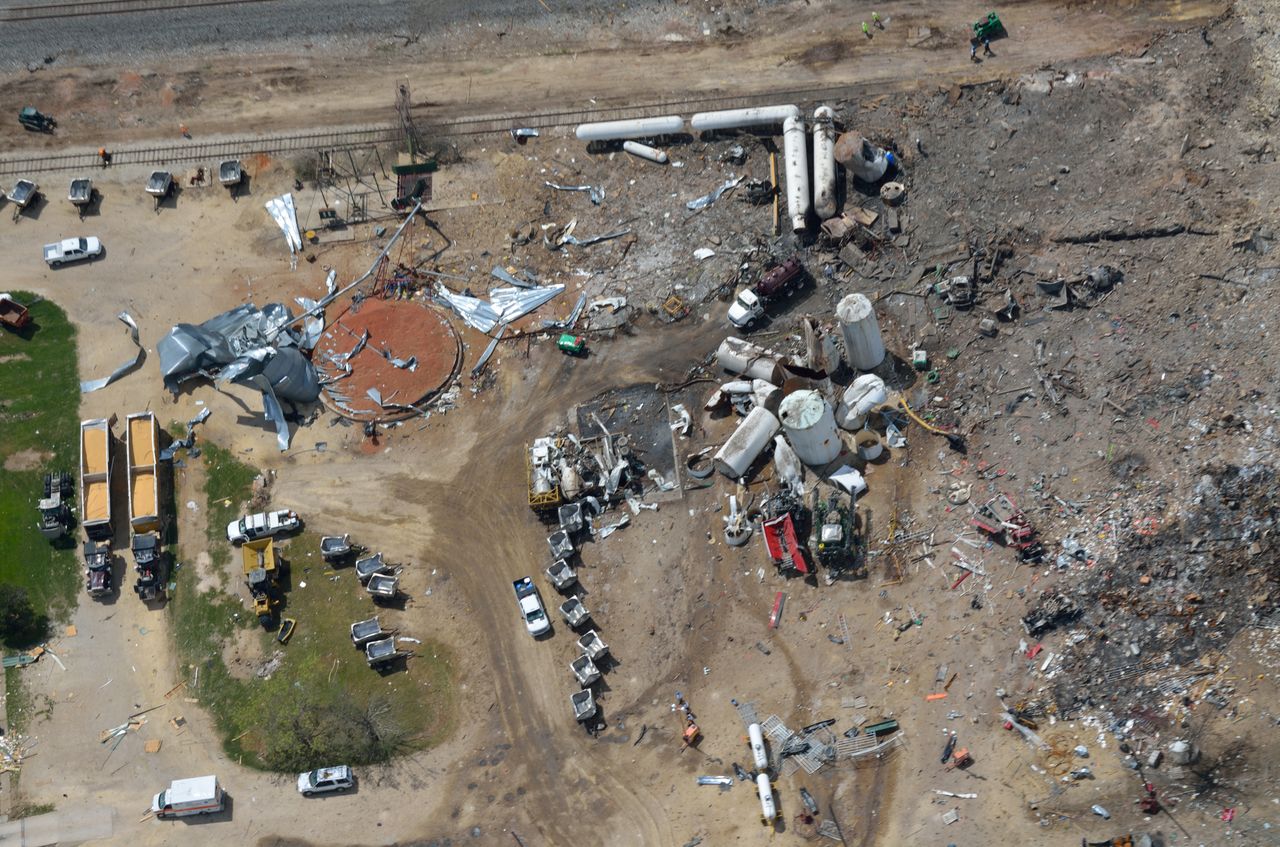

On April 17, 2013, an ammonium nitrate explosion occurred at the West Fertilizer Company storage and distribution facility in West, Texas, eighteen miles (29 km) north of Waco, while emergency services personnel were responding to a fire at the facility. Fifteen people were killed, more than 160 were injured, and more than 150 buildings were damaged or destroyed. Investigators have confirmed that ammonium nitrate was the material that exploded. On May 11, 2016, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives stated that the fire had been deliberately set.
Background
West Fertilizer Company had supplied chemicals to farmers since it was founded in 1962. As of 2013 it was owned by Adair Grain, Inc. and employed nine workers at the facility. Adair Grain, Inc. is wholly owned by Donald Adair and his wife Wanda.
At the time of the incident, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) had last inspected the plant in 1985. According to records obtained by the Associated Press, OSHA cited the plant for improper storage of anhydrous ammonia and fined it $30. OSHA could have fined the company as much as $1,000. OSHA also cited the plant for violations of respiratory protection standards, but did not impose a fine. OSHA officials said the facility was not on their "National Emphasis Plan" for inspections, because it was not a manufacturer, had no record of a major accident, and the Environmental Protection Agency did not consider it a major risk.
After a complaint in 2006 about an ammonia smell coming from the facility, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality investigated and cited the operator for not having a permit for two storage tanks that contained anhydrous ammonia. A permit was issued once the operators brought the facility into accord with agency regulations and recommendations. Also in 2006, the EPA fined the owners $2,300 for problems that included not filing a risk management program plan on time. In June 2012, the U.S. Department of Transportation's Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration further fined the facility $5,250 for violations regarding anhydrous ammonia storage.
According to an open records request by Reuters, the plant had a long history of minor thefts, presumably by people wanting to use anhydrous ammonia to make methamphetamine. The facility lacked burglar alarms, or even a fenced perimeter. It installed a surveillance system in 2009 after law enforcement recommended they do so.
In an emergency planning report filed with the EPA in 2011, company officials said the ammonia storage tanks did not represent a significant fire or explosion hazard. The tanks were still intact following the fire and explosion.
According to its last filing with the EPA in late 2012, the company stated that it stored 540,000 pounds (270 short tons; 240 t) of ammonium nitrate and 110,000 pounds (55 short tons; 50 t) of anhydrous ammonia on the site.[20] A week after the explosion, Homeland Security Secretary Janet Napolitano told Senate investigators that the company did not appear to have disclosed its ammonium nitrate stock to her department. Federal law requires that the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) be notified whenever anyone has more than one ton of ammonium nitrate on hand, or 400 pounds (180 kg) if the ammonium nitrate is combined with combustible material.
Fire and explosion
The facility caught fire on Wednesday, April 17, 2013, and roughly 20 minutes after the fire was first reported to emergency dispatchers the site exploded. At 7:50:38 p.m. CDT (00:50 UTC, April 18), as firefighters were attempting to douse the flames, it exploded with the force of 7.5-10 tons of TNT.
The explosion created a 93 foot wide crater where the site of the fertilizer plant had previously been, and resulted in 12 deaths and numerous injuries.
After weeks of investigation, the cause of the initial fire remained unknown; authorities ruled out weather, natural causes, anhydrous ammonia, and ammonium nitrate in a rail car as possible causes.
In May 2016, the ATF announced that they had determined the fire had been deliberately set.
Aftermath
The massive explosion obliterated the West Fertilizer Company plant and caused heavy damage and further destruction to surrounding areas. Numbers for people dead or injured varied initially.
Damage
In addition to the obliterated plant, the damaged buildings included the public West Middle School, which sits next to the facility. A neighboring 50-unit, two-story apartment building was destroyed.
The blast damaged the nearby West Rest Haven nursing home, and many residents were evacuated. Many of the nursing home residents received cuts from flying glass, but emergency personnel on scene judged that most of these injuries were not life-threatening.
On April 20, some residents who tried to return to their destroyed homes were turned away, because leaking gas tanks were causing small fires.
According to the company's insurer, United States Fire Insurance of Morristown, New Jersey, the facility was only covered by $1 million in liability insurance. According to official estimates from both state and company officials, this amount did not even begin to cover the cost of damages. Furthermore, according to The Dallas Morning News, Texas law allows fertilizer storage facilities to operate without any liability insurance at all, even when they store hazardous materials.
Injuries and fatalities
West Mayor Tommy Muska told the Waco Tribune-Herald that as of late evening, April 17, six or seven volunteer firefighters from the city were unaccounted for. West EMS Director Dr. George Smith, himself injured, said he believed at least two emergency responders were killed.
"We do have confirmed fatalities," Texas Department of Public Safety spokesman D.L. Wilson said at a midnight news conference on April 17. "We have a tremendous amount of injuries ... over 100 injuries at this time." Wilson did not confirm or deny an earlier report that the number of deaths could be in the range of 60 to 70. He said the blast zone was "just like the Murrah Building in Oklahoma City," comparing its effects to the Oklahoma City bombing, and that "50 to 75" homes and businesses were damaged. Sergeant William Patrick Swanton of the Waco Police Department said the operation has gone into a "search-and-rescue mode", aiming to find survivors and recover those who might be trapped in buildings. He said at least 160 people had been injured, and the firefighters who were combating the initial fire were still unaccounted for. Swanton quoted local environmental officials and emergency personnel in saying there was no risk to the community from the smoke fumes rising from the facility.
Over 100 people were reported injured in the blast, and were originally transported to a makeshift triage set up at West High School's football field. It was later moved to a community center due to its proximity to the still-burning facility. Hillcrest Baptist Medical Center in Waco received over 40 injured for treatment. Patients were also admitted to Waco's Providence Healthcare Network, Fort Worth's John Peter Smith Health Network, Dallas's Parkland Memorial Hospital, and Temple's Scott and White Memorial Hospital.
Authorities announced on April 19 that twelve bodies had been recovered, sixty people were missing, and at least 200 had been injured. The twelve dead included ten first responders as well as two civilians who had volunteered to fight the fire.[37]
The final confirmed death toll was fifteen fatalities, and approximately 160 to 200 people were injured.
</snip>

On April 17, 2013, an ammonium nitrate explosion occurred at the West Fertilizer Company storage and distribution facility in West, Texas, eighteen miles (29 km) north of Waco, while emergency services personnel were responding to a fire at the facility. Fifteen people were killed, more than 160 were injured, and more than 150 buildings were damaged or destroyed. Investigators have confirmed that ammonium nitrate was the material that exploded. On May 11, 2016, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives stated that the fire had been deliberately set.
Background
West Fertilizer Company had supplied chemicals to farmers since it was founded in 1962. As of 2013 it was owned by Adair Grain, Inc. and employed nine workers at the facility. Adair Grain, Inc. is wholly owned by Donald Adair and his wife Wanda.
At the time of the incident, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) had last inspected the plant in 1985. According to records obtained by the Associated Press, OSHA cited the plant for improper storage of anhydrous ammonia and fined it $30. OSHA could have fined the company as much as $1,000. OSHA also cited the plant for violations of respiratory protection standards, but did not impose a fine. OSHA officials said the facility was not on their "National Emphasis Plan" for inspections, because it was not a manufacturer, had no record of a major accident, and the Environmental Protection Agency did not consider it a major risk.
After a complaint in 2006 about an ammonia smell coming from the facility, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality investigated and cited the operator for not having a permit for two storage tanks that contained anhydrous ammonia. A permit was issued once the operators brought the facility into accord with agency regulations and recommendations. Also in 2006, the EPA fined the owners $2,300 for problems that included not filing a risk management program plan on time. In June 2012, the U.S. Department of Transportation's Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration further fined the facility $5,250 for violations regarding anhydrous ammonia storage.
According to an open records request by Reuters, the plant had a long history of minor thefts, presumably by people wanting to use anhydrous ammonia to make methamphetamine. The facility lacked burglar alarms, or even a fenced perimeter. It installed a surveillance system in 2009 after law enforcement recommended they do so.
In an emergency planning report filed with the EPA in 2011, company officials said the ammonia storage tanks did not represent a significant fire or explosion hazard. The tanks were still intact following the fire and explosion.
According to its last filing with the EPA in late 2012, the company stated that it stored 540,000 pounds (270 short tons; 240 t) of ammonium nitrate and 110,000 pounds (55 short tons; 50 t) of anhydrous ammonia on the site.[20] A week after the explosion, Homeland Security Secretary Janet Napolitano told Senate investigators that the company did not appear to have disclosed its ammonium nitrate stock to her department. Federal law requires that the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) be notified whenever anyone has more than one ton of ammonium nitrate on hand, or 400 pounds (180 kg) if the ammonium nitrate is combined with combustible material.
Fire and explosion
The facility caught fire on Wednesday, April 17, 2013, and roughly 20 minutes after the fire was first reported to emergency dispatchers the site exploded. At 7:50:38 p.m. CDT (00:50 UTC, April 18), as firefighters were attempting to douse the flames, it exploded with the force of 7.5-10 tons of TNT.
The explosion created a 93 foot wide crater where the site of the fertilizer plant had previously been, and resulted in 12 deaths and numerous injuries.
After weeks of investigation, the cause of the initial fire remained unknown; authorities ruled out weather, natural causes, anhydrous ammonia, and ammonium nitrate in a rail car as possible causes.
In May 2016, the ATF announced that they had determined the fire had been deliberately set.
Aftermath
The massive explosion obliterated the West Fertilizer Company plant and caused heavy damage and further destruction to surrounding areas. Numbers for people dead or injured varied initially.
Damage
In addition to the obliterated plant, the damaged buildings included the public West Middle School, which sits next to the facility. A neighboring 50-unit, two-story apartment building was destroyed.
The blast damaged the nearby West Rest Haven nursing home, and many residents were evacuated. Many of the nursing home residents received cuts from flying glass, but emergency personnel on scene judged that most of these injuries were not life-threatening.
On April 20, some residents who tried to return to their destroyed homes were turned away, because leaking gas tanks were causing small fires.
According to the company's insurer, United States Fire Insurance of Morristown, New Jersey, the facility was only covered by $1 million in liability insurance. According to official estimates from both state and company officials, this amount did not even begin to cover the cost of damages. Furthermore, according to The Dallas Morning News, Texas law allows fertilizer storage facilities to operate without any liability insurance at all, even when they store hazardous materials.
Injuries and fatalities
West Mayor Tommy Muska told the Waco Tribune-Herald that as of late evening, April 17, six or seven volunteer firefighters from the city were unaccounted for. West EMS Director Dr. George Smith, himself injured, said he believed at least two emergency responders were killed.
"We do have confirmed fatalities," Texas Department of Public Safety spokesman D.L. Wilson said at a midnight news conference on April 17. "We have a tremendous amount of injuries ... over 100 injuries at this time." Wilson did not confirm or deny an earlier report that the number of deaths could be in the range of 60 to 70. He said the blast zone was "just like the Murrah Building in Oklahoma City," comparing its effects to the Oklahoma City bombing, and that "50 to 75" homes and businesses were damaged. Sergeant William Patrick Swanton of the Waco Police Department said the operation has gone into a "search-and-rescue mode", aiming to find survivors and recover those who might be trapped in buildings. He said at least 160 people had been injured, and the firefighters who were combating the initial fire were still unaccounted for. Swanton quoted local environmental officials and emergency personnel in saying there was no risk to the community from the smoke fumes rising from the facility.
Over 100 people were reported injured in the blast, and were originally transported to a makeshift triage set up at West High School's football field. It was later moved to a community center due to its proximity to the still-burning facility. Hillcrest Baptist Medical Center in Waco received over 40 injured for treatment. Patients were also admitted to Waco's Providence Healthcare Network, Fort Worth's John Peter Smith Health Network, Dallas's Parkland Memorial Hospital, and Temple's Scott and White Memorial Hospital.
Authorities announced on April 19 that twelve bodies had been recovered, sixty people were missing, and at least 200 had been injured. The twelve dead included ten first responders as well as two civilians who had volunteered to fight the fire.[37]
The final confirmed death toll was fifteen fatalities, and approximately 160 to 200 people were injured.
</snip>
I didn't realize that the West, TX explosion took place a day after the 66th anniversary of the Texas City Disaster.
April 16, 2019
72 Years Ago Today; The Texas City Disaster
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Texas_City_disaster

The Texas City disaster was an industrial accident that occurred April 16, 1947 in the Port of Texas City, Texas. It was the deadliest industrial accident in U.S. history, and one of history's largest non-nuclear explosions. Originating with a mid-morning fire on board the French-registered vessel SS Grandcamp (docked in the port), her cargo of approximately 2,200 tons (approximately 2,100 metric tons) of ammonium nitrate detonated, initiating a subsequent chain-reaction of additional fires and explosions in other ships and nearby oil-storage facilities. It killed at least 581 people, including all but one member of the Texas City fire department. The disaster triggered the first ever class action lawsuit against the United States government, under the then-recently enacted Federal Tort Claims Act (FTCA), on behalf of 8,485 victims.
<snip>
Explosions
The ammonium nitrate, needed either as fertilizer or an explosive, was manufactured in Nebraska and Iowa and shipped to Texas City by rail before being loaded on the Grandcamp. It was manufactured in a patented process, mixed with clay, petrolatum, rosin and paraffin wax to avoid moisture caking. It was also packaged in paper sacks, then transported and stored at temperatures that increased its chemical activity. Longshoremen reported the bags were warm to the touch before loading.
On April 16, 1947, around 8:00 a.m. smoke was spotted in the cargo hold of the Grandcamp while she was still moored. Over the next hour, attempts to extinguish the fire or bring it under control failed as a red glow returned after each effort to douse the fire.
Shortly before 9:00 a.m., the captain ordered his men to steam the hold, a firefighting method where steam is piped in to extinguish fires, to preserve the cargo. This was unlikely to be effective, as ammonium nitrate produces its own oxygen, thus neutralizing the extinguishing properties of steam. The steam may have contributed to the fire by converting the ammonium nitrate to nitrous oxide, while augmenting the already intense heat in the ship's hold.
The fire attracted spectators along the shoreline, who believed they were at a safe distance. Eventually, the steam pressure inside the ship blew the hatches open, and yellow-orange smoke billowed out. This color is typical for nitrogen dioxide fumes. The unusual color of the smoke attracted more spectators. Spectators also noted that the water around the docked ship was boiling from the heat, and the splashing water touching the hull was being vaporized into steam. The cargo hold and deck began to bulge as the pressure of the steam increased inside.
At 9:12 a.m., the ammonium nitrate reached an explosive threshold from the combination of heat and pressure. The vessel then detonated, causing great destruction and damage throughout the port. The tremendous blast sent a 15-foot (4.5 m) wave that was detectable nearly 100 miles (160 km) off the Texas shoreline. The blast leveled nearly 1,000 buildings on land. The Grandcamp explosion destroyed the Monsanto Chemical Company plant and resulted in ignition of refineries and chemical tanks on the waterfront. Falling bales of burning twine from the ship's cargo added to the damage while the Grandcamp's anchor was hurled across the city. Two sightseeing airplanes flying nearby had their wings shorn off, forcing them out of the sky. 10 miles (16 km) away, half of the windows in Galveston were shattered. The explosion blew almost 6,350 short tons (5,760 metric tons) of the ship's steel into the air, some at supersonic speed. Official casualty estimates came to a total of 567, including all the crewmen who remained aboard the Grandcamp. All but one member of the 28-man Texas City volunteer fire department were killed in the initial explosion on the docks while fighting the shipboard fire. With fires raging throughout Texas City, first responders from other areas were initially unable to reach the site of the disaster.
The first explosion ignited ammonium nitrate in the nearby cargo ship High Flyer. The crews spent hours attempting to cut the High Flyer free from her anchor and other obstacles, without success. After smoke had been pouring from the hold for over five hours, and about 15 hours after the explosions aboard the Grandcamp, the High Flyer exploded, demolishing the nearby SS Wilson B. Keene, killing at least two more and increasing the damage to the port and other ships with more shrapnel and burning material. One of the propellers on the High Flyer was blown off and subsequently found nearly a mile inland. It is now part of a memorial park and sits near the anchor of the Grandcamp. The propeller is cracked in several places, and one blade has a large piece missing.
The cause of the initial fire on board the Grandcamp was never determined, but it may have been started by a cigarette discarded the previous day, meaning the ship's cargo had been smouldering throughout the night when it was discovered on the morning of the day of the explosion.
Scale of the disaster
The Texas City disaster is generally considered the worst industrial accident in American history. Witnesses compared the scene to the fairly recent images of the 1943 air raid on Bari and the much larger devastation at Nagasaki. Of the dead, 405 were identified and 63 have never been identified. These were placed in a memorial cemetery in the north part of Texas City near Moses Lake. An additional 113 people were classified as missing, for no identifiable parts were ever found. This figure includes firefighters who were aboard Grandcamp when she exploded. There is some speculation that there may have been hundreds more killed but uncounted, including visiting seamen, non-census laborers and their families, and an untold number of travelers. However, there were some survivors as close as 70 feet (21 m) from the dock. The victims' bodies quickly filled the local morgue, and several bodies were laid out in the local high school's gymnasium for identification by loved ones.

Parking lot 1?4 mile (0.40 km) away from the explosion
More than 5,000 people were injured, with 1,784 admitted to 21 area hospitals. More than 500 homes were destroyed and hundreds damaged, leaving 2,000 homeless. The seaport was destroyed, and many businesses were flattened or burned. Over 1,100 vehicles were damaged and 362 freight cars were obliterated—the property damage was estimated at $100 million[7] (equivalent to $1,100,000,000 in 2018).
A 2-short-ton (1.8-metric-ton) anchor of Grandcamp was hurled 1.62 miles (2.61 km) and found in a 10-foot (3 m) crater. It now rests in a memorial park. The other main 5-short-ton (4.5-metric-ton) anchor was hurled 1?2 mile (800 m) to the entrance of the Texas City Dike, and rests on a "Texas-shaped" memorial at the entrance. Burning wreckage ignited everything within miles, including dozens of oil storage tanks and chemical tanks. The nearby city of Galveston, Texas, was covered with an oily fog which left deposits over every exposed outdoor surface.
Firefighting casualties
Some of the deaths and damage in Texas City were due to the destruction and subsequent burning of several chemical plants (including Monsanto and Union Carbide), oil storage, and other facilities near the explosions. 27 of the 28 members of Texas City's volunteer fire department and 3 of 4 members of the Texas City Heights Volunteer Fire Department who were on the docks near the burning ship were killed. One firefighter, Fred Dowdy, who had not responded to the initial call, coordinated other firefighters arriving from communities up to 60 miles (100 km) away. Alvin Fussell, sole survivor of the Heights Volunteer fire fighters, was driving to work in Alvin when he heard of the fire on the radio. Eventually 200 firefighters arrived, from as far away as Los Angeles. Fires resulting from the cataclysmic events were still burning a week after the disaster, and the process of body recovery took nearly a month. All four fire engines of Texas City were twisted and burned hulks.
</snip>

The Texas City disaster was an industrial accident that occurred April 16, 1947 in the Port of Texas City, Texas. It was the deadliest industrial accident in U.S. history, and one of history's largest non-nuclear explosions. Originating with a mid-morning fire on board the French-registered vessel SS Grandcamp (docked in the port), her cargo of approximately 2,200 tons (approximately 2,100 metric tons) of ammonium nitrate detonated, initiating a subsequent chain-reaction of additional fires and explosions in other ships and nearby oil-storage facilities. It killed at least 581 people, including all but one member of the Texas City fire department. The disaster triggered the first ever class action lawsuit against the United States government, under the then-recently enacted Federal Tort Claims Act (FTCA), on behalf of 8,485 victims.
<snip>
Explosions
The ammonium nitrate, needed either as fertilizer or an explosive, was manufactured in Nebraska and Iowa and shipped to Texas City by rail before being loaded on the Grandcamp. It was manufactured in a patented process, mixed with clay, petrolatum, rosin and paraffin wax to avoid moisture caking. It was also packaged in paper sacks, then transported and stored at temperatures that increased its chemical activity. Longshoremen reported the bags were warm to the touch before loading.
On April 16, 1947, around 8:00 a.m. smoke was spotted in the cargo hold of the Grandcamp while she was still moored. Over the next hour, attempts to extinguish the fire or bring it under control failed as a red glow returned after each effort to douse the fire.
Shortly before 9:00 a.m., the captain ordered his men to steam the hold, a firefighting method where steam is piped in to extinguish fires, to preserve the cargo. This was unlikely to be effective, as ammonium nitrate produces its own oxygen, thus neutralizing the extinguishing properties of steam. The steam may have contributed to the fire by converting the ammonium nitrate to nitrous oxide, while augmenting the already intense heat in the ship's hold.
The fire attracted spectators along the shoreline, who believed they were at a safe distance. Eventually, the steam pressure inside the ship blew the hatches open, and yellow-orange smoke billowed out. This color is typical for nitrogen dioxide fumes. The unusual color of the smoke attracted more spectators. Spectators also noted that the water around the docked ship was boiling from the heat, and the splashing water touching the hull was being vaporized into steam. The cargo hold and deck began to bulge as the pressure of the steam increased inside.
At 9:12 a.m., the ammonium nitrate reached an explosive threshold from the combination of heat and pressure. The vessel then detonated, causing great destruction and damage throughout the port. The tremendous blast sent a 15-foot (4.5 m) wave that was detectable nearly 100 miles (160 km) off the Texas shoreline. The blast leveled nearly 1,000 buildings on land. The Grandcamp explosion destroyed the Monsanto Chemical Company plant and resulted in ignition of refineries and chemical tanks on the waterfront. Falling bales of burning twine from the ship's cargo added to the damage while the Grandcamp's anchor was hurled across the city. Two sightseeing airplanes flying nearby had their wings shorn off, forcing them out of the sky. 10 miles (16 km) away, half of the windows in Galveston were shattered. The explosion blew almost 6,350 short tons (5,760 metric tons) of the ship's steel into the air, some at supersonic speed. Official casualty estimates came to a total of 567, including all the crewmen who remained aboard the Grandcamp. All but one member of the 28-man Texas City volunteer fire department were killed in the initial explosion on the docks while fighting the shipboard fire. With fires raging throughout Texas City, first responders from other areas were initially unable to reach the site of the disaster.
The first explosion ignited ammonium nitrate in the nearby cargo ship High Flyer. The crews spent hours attempting to cut the High Flyer free from her anchor and other obstacles, without success. After smoke had been pouring from the hold for over five hours, and about 15 hours after the explosions aboard the Grandcamp, the High Flyer exploded, demolishing the nearby SS Wilson B. Keene, killing at least two more and increasing the damage to the port and other ships with more shrapnel and burning material. One of the propellers on the High Flyer was blown off and subsequently found nearly a mile inland. It is now part of a memorial park and sits near the anchor of the Grandcamp. The propeller is cracked in several places, and one blade has a large piece missing.
The cause of the initial fire on board the Grandcamp was never determined, but it may have been started by a cigarette discarded the previous day, meaning the ship's cargo had been smouldering throughout the night when it was discovered on the morning of the day of the explosion.
Scale of the disaster
The Texas City disaster is generally considered the worst industrial accident in American history. Witnesses compared the scene to the fairly recent images of the 1943 air raid on Bari and the much larger devastation at Nagasaki. Of the dead, 405 were identified and 63 have never been identified. These were placed in a memorial cemetery in the north part of Texas City near Moses Lake. An additional 113 people were classified as missing, for no identifiable parts were ever found. This figure includes firefighters who were aboard Grandcamp when she exploded. There is some speculation that there may have been hundreds more killed but uncounted, including visiting seamen, non-census laborers and their families, and an untold number of travelers. However, there were some survivors as close as 70 feet (21 m) from the dock. The victims' bodies quickly filled the local morgue, and several bodies were laid out in the local high school's gymnasium for identification by loved ones.

Parking lot 1?4 mile (0.40 km) away from the explosion
More than 5,000 people were injured, with 1,784 admitted to 21 area hospitals. More than 500 homes were destroyed and hundreds damaged, leaving 2,000 homeless. The seaport was destroyed, and many businesses were flattened or burned. Over 1,100 vehicles were damaged and 362 freight cars were obliterated—the property damage was estimated at $100 million[7] (equivalent to $1,100,000,000 in 2018).
A 2-short-ton (1.8-metric-ton) anchor of Grandcamp was hurled 1.62 miles (2.61 km) and found in a 10-foot (3 m) crater. It now rests in a memorial park. The other main 5-short-ton (4.5-metric-ton) anchor was hurled 1?2 mile (800 m) to the entrance of the Texas City Dike, and rests on a "Texas-shaped" memorial at the entrance. Burning wreckage ignited everything within miles, including dozens of oil storage tanks and chemical tanks. The nearby city of Galveston, Texas, was covered with an oily fog which left deposits over every exposed outdoor surface.
Firefighting casualties
Some of the deaths and damage in Texas City were due to the destruction and subsequent burning of several chemical plants (including Monsanto and Union Carbide), oil storage, and other facilities near the explosions. 27 of the 28 members of Texas City's volunteer fire department and 3 of 4 members of the Texas City Heights Volunteer Fire Department who were on the docks near the burning ship were killed. One firefighter, Fred Dowdy, who had not responded to the initial call, coordinated other firefighters arriving from communities up to 60 miles (100 km) away. Alvin Fussell, sole survivor of the Heights Volunteer fire fighters, was driving to work in Alvin when he heard of the fire on the radio. Eventually 200 firefighters arrived, from as far away as Los Angeles. Fires resulting from the cataclysmic events were still burning a week after the disaster, and the process of body recovery took nearly a month. All four fire engines of Texas City were twisted and burned hulks.
</snip>
Profile Information
Member since: Wed Oct 15, 2008, 06:29 PMNumber of posts: 18,770